Main Difference
The main difference between Urea and Uric Acid is that the Urea is a chemical compound and Uric Acid is a the end product of nucleic acid degradation.
-
Urea
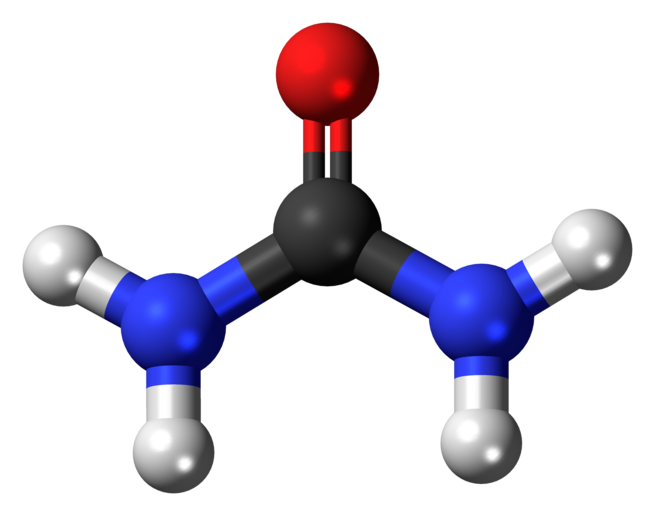
Urea, also known as carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula CO(NH2)2. This amide has two –NH2 groups joined by a carbonyl (C=O) functional group.
Urea serves an important role in the metabolism of nitrogen-containing compounds by animals and is the main nitrogen-containing substance in the urine of mammals. It is a colorless, odorless solid, highly soluble in water, and practically non-toxic (LD50 is 15 g/kg for rats). Dissolved in water, it is neither acidic nor alkaline. The body uses it in many processes, most notably nitrogen excretion. The liver forms it by combining two ammonia molecules (NH3) with a carbon dioxide (CO2) molecule in the urea cycle. Urea is widely used in fertilizers as a source of nitrogen and is an important raw material for the chemical industry.
Friedrich Wöhler’s discovery in 1828 that urea can be produced from inorganic starting materials was an important conceptual milestone in chemistry. It showed for the first time that a substance previously known only as a byproduct of life could be synthesized in the laboratory without biological starting materials, contradicting the widely held doctrine of vitalism.
-
Uric Acid
Uric acid is a heterocyclic compound of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen with the formula C5H4N4O3. It forms ions and salts known as urates and acid urates, such as ammonium acid urate. Uric acid is a product of the metabolic breakdown of purine nucleotides, and it is a normal component of urine. High blood concentrations of uric acid can lead to gout and are associated with other medical conditions, including diabetes and the formation of ammonium acid urate kidney stones.
-
Urea (noun)
A water-soluble organic compound, CO(NH2)2, formed by the metabolism of proteins and excreted in the urine.
-
Urea (noun)
Any N-substituted derivative of urea, with the general formula (R1R2N)CO(NR3R4).
