Main Difference
The main difference between Positive Feedback and Negative Feedback is that the Positive Feedback is a process that occurs in a feedback loop which magnifies a small disturbance and Negative Feedback is a stability mechanism which occurs when some function of the output of a system, process, mechanism is fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused by changes in the input or by other disturbances
-
Positive Feedback
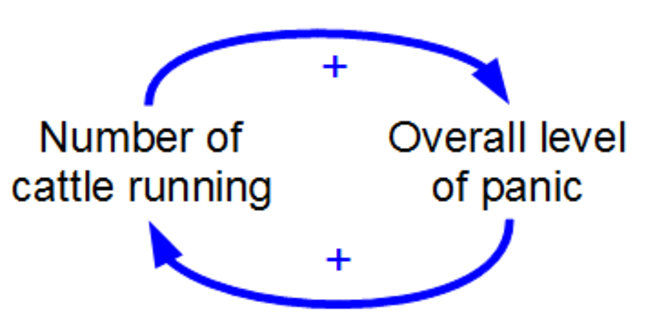
Positive feedback (exacerbating feedback, self-reinforcing feedback) is a process that occurs in a feedback loop which exacerbates the effects of a small disturbance. That is, the effects of a perturbation on a system include an increase in the magnitude of the perturbation. That is, A produces more of B which in turn produces more of A. In contrast, a system in which the results of a change act to reduce or counteract it has negative feedback. Both concepts play an important role in science and engineering, including biology, chemistry, and cybernetics.
Mathematically, positive feedback is defined as a positive loop gain around a closed loop of cause and effect.
That is, positive feedback is in phase with the input, in the sense that it adds to make the input larger.
Positive feedback tends to cause system instability. When the loop gain is positive and above 1, there will typically be exponential growth, increasing oscillations, chaotic behavior or other divergences from equilibrium. System parameters will typically accelerate towards extreme values, which may damage or destroy the system, or may end with the system latched into a new stable state. Positive feedback may be controlled by signals in the system being filtered, damped, or limited, or it can be cancelled or reduced by adding negative feedback.
Positive feedback is used in digital electronics to force voltages away from intermediate voltages into ‘0’ and ‘1’ states. On the other hand, thermal runaway is a type of positive feedback that can destroy semiconductor junctions. Positive feedback in chemical reactions can increase the rate of reactions, and in some cases can lead to explosions. Positive feedback in mechanical design causes tipping-point, or ‘over-centre’, mechanisms to snap into position, for example in switches and locking pliers. Out of control, it can cause bridges to collapse. Positive feedback in economic systems can cause boom-then-bust cycles. A familiar example of positive feedback is the loud squealing or howling sound produced by audio feedback in public address systems: the microphone picks up sound from its own loudspeakers, amplifies it, and sends it through the speakers again.
-
Negative Feedback
Negative feedback (or balancing feedback) occurs when some function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused by changes in the input or by other disturbances.
Whereas positive feedback tends to lead to instability via exponential growth, oscillation or chaotic behavior, negative feedback generally promotes stability. Negative feedback tends to promote a settling to equilibrium, and reduces the effects of perturbations. Negative feedback loops in which just the right amount of correction is applied with optimum timing can be very stable, accurate, and responsive.
Negative feedback is widely used in mechanical and electronic engineering, and also within living organisms, and can be seen in many other fields from chemistry and economics to physical systems such as the climate. General negative feedback systems are studied in control systems engineering.
Negative feedback loops also play an integral role in maintaining the atmospheric balance in various systems on Earth. One such feedback system is the interaction between solar radiation, cloud cover, and planet temperature.
