Main Difference
The main difference between Placenta and Umbilical Cord is that the Placenta is a organ that connects the developing foetus to the uterine wall and Umbilical Cord is a conduit between embryo/fetus and the placenta
-
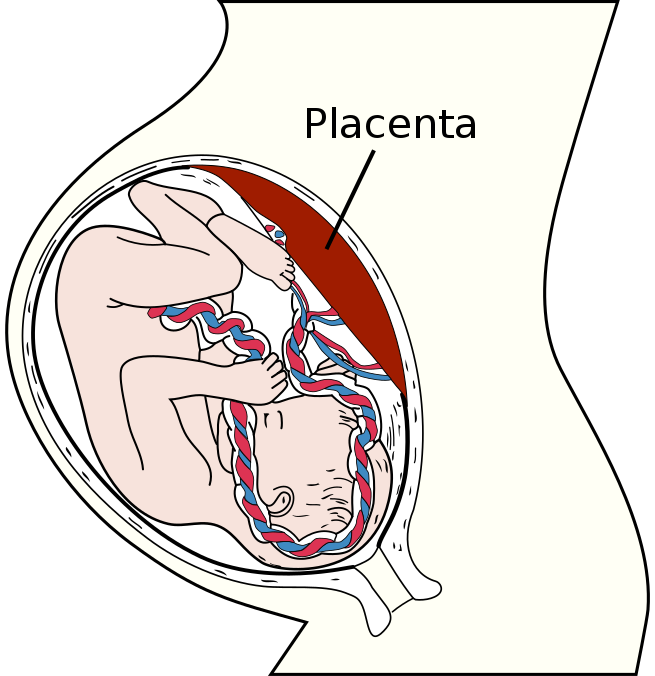
Placenta
The placenta is a temporary organ that connects the developing fetus via the umbilical cord to the uterine wall to allow nutrient uptake, thermo-regulation, waste elimination, and gas exchange via the mother’s blood supply; to fight against internal infection; and to produce hormones which support pregnancy. Placentas are a defining characteristic of placental mammals, but are also found in marsupials and some non-mammals with varying levels of development.The placenta functions as a fetomaternal organ with two components: the fetal placenta (Chorion frondosum), which develops from the same blastocyst that forms the fetus, and the maternal placenta (Decidua basalis), which develops from the maternal uterine tissue. It metabolizes a number of substances and can release metabolic products into maternal or fetal circulations. The placenta is expelled from the body upon birth of the fetus.
The word placenta comes from the Latin word for a type of cake, from Greek πλακόεντα/πλακοῦντα plakóenta/plakoúnta, accusative of πλακόεις/πλακούς plakóeis/plakoús, “flat, slab-like”, in reference to its round, flat appearance in humans. The classical plural is placentae, but the form placentas is common in modern English and probably has the wider currency at present.
-
Umbilical Cord
In placental mammals, the umbilical cord (also called the navel string, birth cord or funiculus umbilicalis) is a conduit between the developing embryo or fetus and the placenta. During prenatal development, the umbilical cord is physiologically and genetically part of the fetus and (in humans) normally contains two arteries (the umbilical arteries) and one vein (the umbilical vein), buried within Wharton’s jelly. The umbilical vein supplies the fetus with oxygenated, nutrient-rich blood from the placenta. Conversely, the fetal heart pumps low oxygen containing blood, nutrient-depleted blood through the umbilical arteries back to the placenta.
-
Placenta (noun)
A vascular organ in mammals, except monotremes and marsupials, present only in the female during gestation. It supplies food and oxygen from the mother to the foetus, and passes back waste. It is implanted in the wall of the uterus and links to the foetus through the umbilical cord. It is expelled after birth.
-
Placenta (noun)
In flowering plants, the part of the ovary where ovules develop; in non-flowering plants where the spores develop.
-
Placenta (noun)
a flattened circular organ in the uterus of pregnant eutherian mammals, nourishing and maintaining the fetus through the umbilical cord.
-
Placenta (noun)
(in flowers) part of the ovary wall to which the ovules are attached.
