-
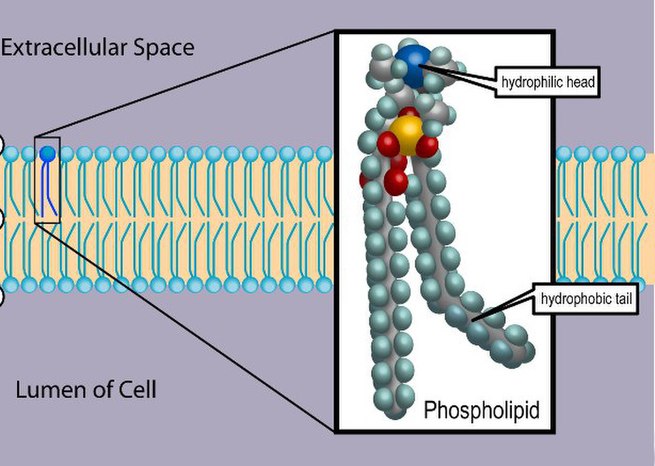
Phospholipid
Phospholipids are a class of lipids that are a major component of all cell membranes. They can form lipid bilayers because of their amphiphilic characteristic. The structure of the phospholipid molecule generally consists of two hydrophobic fatty acid “tails” and a hydrophilic “head” consisting of a phosphate group. The two components are joined together by a glycerol molecule. The phosphate groups can be modified with simple organic molecules such as choline, ethanolamine or serine.
The first phospholipid identified in 1847 as such in biological tissues was lecithin, or phosphatidylcholine, in the egg yolk of chickens by the French chemist and pharmacist, Theodore Nicolas Gobley. Biological membranes in eukaryotes also contain another class of lipid, sterol, interspersed among the phospholipids and together they provide membrane fluidity and mechanical strength. Purified phospholipids are produced commercially and have found applications in nanotechnology and materials science.
-
Triglyceride
A triglyceride (TG, triacylglycerol, TAG, or triacylglyceride) is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids (from tri- and glyceride). Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other animals, as well as vegetable fat. They are also present in the blood to enable the bidirectional transference of adipose fat and blood glucose from the liver, and are a major component of human skin oils.
There are many different types of triglyceride, with the main division between saturated and unsaturated types. Saturated fats are “saturated” with hydrogen — all available places where hydrogen atoms could be bonded to carbon atoms are occupied. These have a higher melting point and are more likely to be solid at room temperature. Unsaturated fats have double bonds between some of the carbon atoms, reducing the number of places where hydrogen atoms can bond to carbon atoms. These have a lower melting point and are more likely to be liquid at room temperature.
-
Phospholipid (noun)
Any lipid, such as lecithin or cephalin, consisting of a diglyceride combined with a phosphate group and a simple organic molecule such as choline or ethanolamine; they are important constituents of biological membranes.
-
Triglyceride (noun)
A lipid, an ester of glycerol and three fatty acids (the same or different); the major constituent of animal and vegetable fats.
-
Phospholipid (noun)
a lipid containing a phosphate group in its molecule, e.g. phosphatidylcholine.
-
Triglyceride (noun)
an ester formed from glycerol and three fatty acid groups. Triglycerides are the main constituents of natural fats and oils.
