Main Difference
The main difference between Nylon and Polyester is that the Nylon is a family of synthetic polymers originally developed as textile fibers and Polyester is a category of polymers.
-
Nylon
Nylon is a generic designation for a family of synthetic polymers, based on aliphatic or semi-aromatic polyamides.
Nylon is a thermoplastic silky material
that can be melt-processed into fibers, films or shapes.Nylon was the first commercially successful synthetic thermoplastic polymer. DuPont began its research project in 1930.
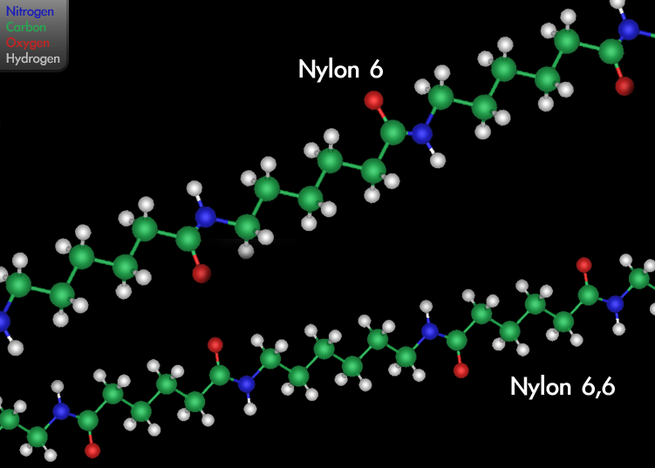
The first example of nylon (nylon 6,6) was produced using diamines on February 28, 1935, by Wallace Hume Carothers at DuPont’s research facility at the DuPont Experimental Station. In response to Carothers’ work, Paul Schlack at IG Farben developed nylon 6, a different molecule based on caprolactam, on January 29, 1938.Nylon was first used commercially in a nylon-bristled toothbrush in 1938, followed more famously in women’s stockings or “nylons” which were shown at the 1939 New York World’s Fair and first sold commercially in 1940. During World War II, almost all nylon production was diverted to the military for use in parachutes and parachute cord. Wartime uses of nylon and other plastics greatly increased the market for the new materials.Nylon is made of repeating units linked by amide links similar to the peptide bonds in proteins.
Commercially, nylon polymer is made by reacting monomers which are either lactams, acid/amines or stoichiometric mixtures of diamines (-NH2) and diacids (-COOH). Mixtures of these can be polymerized together to make copolymers. Nylon polymers can be mixed with a wide variety of additives to achieve many different property variations.
Nylon polymers have found significant commercial applications in fabric and fibers (apparel, flooring and rubber reinforcement), in shapes (molded parts for cars, electrical equipment, etc.), and in films (mostly for food packaging).
-
Polyester
Polyester is a category of polymers that contain the ester functional group in their main chain. As a specific material, it most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyesters include naturally occurring chemicals, such as in the cutin of plant cuticles, as well as synthetics such as polybutyrate. Natural polyesters and a few synthetic ones are biodegradable, but most synthetic polyesters are not. The material is used extensively in clothing.
Depending on the chemical structure, polyester can be a thermoplastic or thermoset. There are also polyester resins cured by hardeners; however, the most common polyesters are thermoplastics. Examples of thermoset polyesters include the Desmophen brand from Bayer. The OH group is reacted with an Isocyanate functional compound in a 2 component system producing coatings which may optionally be pigmented.
Fabrics woven or knitted from polyester thread or yarn are used extensively in apparel and home furnishings, from shirts and pants to jackets and hats, bed sheets, blankets, upholstered furniture and computer mouse mats. Industrial polyester fibers, yarns and ropes are used in car tire reinforcements, fabrics for conveyor belts, safety belts, coated fabrics and plastic reinforcements with high-energy absorption. Polyester fiber is used as cushioning and insulating material in pillows, comforters and upholstery padding. Polyester fabrics are highly stain-resistant—in fact, the only class of dyes which can be used to alter the color of polyester fabric are what are known as disperse dyes.Polyester fibers are sometimes spun together with natural fibers to produce a cloth with blended properties. Cotton-polyester blends (polycotton) can be strong, wrinkle and tear-resistant, and reduce shrinking. Synthetic fibers using polyester have high water, wind and environmental resistance compared to plant-derived fibers. They are less fire resistant and can melt when ignited.Polyester blends have been renamed so as to suggest their similarity or even superiority to natural fibers (for example, China silk, which is a term in the textiles industry for a 100% polyester fiber woven to resemble the sheen and durability of insect-derived silk).
Polyesters are also used to make bottles, films, tarpaulin, canoes, liquid crystal displays, holograms, filters, dielectric film for capacitors, film insulation for wire and insulating tapes. Polyesters are widely used as a finish on high-quality wood products such as guitars, pianos and vehicle/yacht interiors. Thixotropic properties of spray-applicable polyesters make them ideal for use on open-grain timbers, as they can quickly fill wood grain, with a high-build film thickness per coat. Cured polyesters can be sanded and polished to a high-gloss, durable finish.
Liquid crystalline polyesters are among the first industrially used liquid crystal polymers. They are used for their mechanical properties and heat-resistance. These traits are also important in their application as an abradable seal in jet engines.
Natural polyesters could have a played a significant role in the origins of life. Long heterogeneous polyester chains are known to easily form in a one-pot reaction without catalyst under simple prebiotic conditions.
-
Nylon (noun)
Originally, the DuPont company trade name for polyamide, a copolymer whose molecules consist of alternating diamine and dicarboxylic acid monomers bonded together; now generically used for this type of polymer.
-
Nylon (noun)
A stocking originally fabricated from nylon; also used generically for any long, sheer stocking worn on a woman’s legs.
“They left the strip club when they discovered the ladies only stripped down to their nylons.”
-
Polyester (noun)
Any polymer whose monomers are linked together by ester bonds
-
Polyester (noun)
A material or fabric made from polyester polymer
-
Polyester (adjective)
Of, or consisting of polyesters
-
Polyester (noun)
a synthetic resin in which the polymer units are linked by ester groups, used chiefly to make synthetic textile fibres.
-
Polyester (noun)
a fabric made from polyester fibre
“dresses in printed polyesters”
“swimwear in a range of fabrics including polyester and silk”