Main Difference
The main difference between Irradiation and Radiation is that the Irradiation is a process by which an object is exposed to radiation and Radiation is a waves or particles propagating through space or through a medium, carrying energy.
-
Irradiation
Irradiation is the process by which an object is exposed to radiation. The exposure can originate from various sources, including natural sources. Most frequently the term refers to ionizing radiation, and to a level of radiation that will serve a specific purpose, rather than radiation exposure to normal levels of background radiation. The term irradiation usually excludes the exposure to non-ionizing radiation, such as infrared, visible light, microwaves from cellular phones or electromagnetic waves emitted by radio and TV receivers and power supplies.
-
Radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or through a material medium. This includes:
electromagnetic radiation, such as radio waves, microwaves, visible light, x-rays, and gamma radiation (γ)
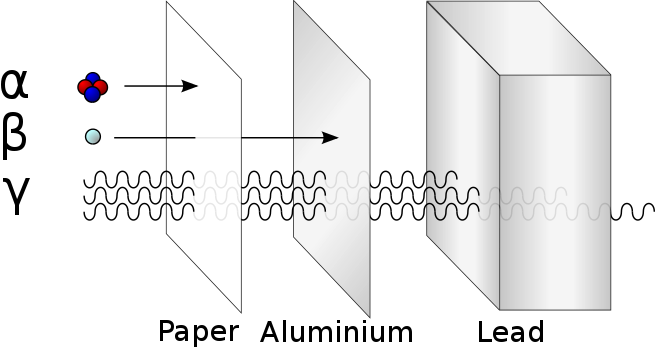
particle radiation, such as alpha radiation (α), beta radiation (β), and neutron radiation (particles of non-zero rest energy)
acoustic radiation, such as ultrasound, sound, and seismic waves (dependent on a physical transmission medium)
gravitational radiation, radiation that takes the form of gravitational waves, or ripples in the curvature of spacetime.
Radiation is often categorized as either ionizing or non-ionizing depending on the energy of the radiated particles. Ionizing radiation carries more than 10 eV, which is enough to ionize atoms and molecules, and break chemical bonds. This is an important distinction due to the large difference in harmfulness to living organisms. A common source of ionizing radiation is radioactive materials that emit α, β, or γ radiation, consisting of helium nuclei, electrons or positrons, and photons, respectively. Other sources include X-rays from medical radiography examinations and muons, mesons, positrons, neutrons and other particles that constitute the secondary cosmic rays that are produced after primary cosmic rays interact with Earth’s atmosphere.
Gamma rays, X-rays and the higher energy range of ultraviolet light constitute the ionizing part of the electromagnetic spectrum. The lower-energy, longer-wavelength part of the spectrum including visible light, infrared light, microwaves, and radio waves is non-ionizing; its main effect when interacting with tissue is heating. This type of radiation only damages cells if the intensity is high enough to cause excessive heating. Ultraviolet radiation has some features of both ionizing and non-ionizing radiation. While the part of the ultraviolet spectrum that penetrates the Earth’s atmosphere is non-ionizing, this radiation does far more damage to many molecules in biological systems than can be accounted for by heating effects, sunburn being a well-known example. These properties derive from ultraviolet’s power to alter chemical bonds, even without having quite enough energy to ionize atoms.
The word radiation arises from the phenomenon of waves radiating (i.e., traveling outward in all directions) from a source. This aspect leads to a system of measurements and physical units that are applicable to all types of radiation. Because such radiation expands as it passes through space, and as its energy is conserved (in vacuum). The intensity of all types of radiation from a point source follows an inverse-square law in relation to the distance from its source. Like any ideal law, the inverse-square law approximates a measured radiation intensity to the extent that the source approximates a geometric point.
-
Irradiation (noun)
An act of irradiating, or state of being irradiated.
-
Irradiation (noun)
illumination; irradiance; brilliance.
-
Irradiation (noun)
mental light or illumination.
-
Irradiation (noun)
The apparent enlargement of a bright object seen upon a dark ground, due to the fact that the portions of the retina around the image are stimulated by the intense light; as when a dark spot on a white ground appears smaller, or a white spot on a dark ground larger, than it really is, especially when a little out of focus.
-
Irradiation (noun)
a process of sterilisation whereby radiation is passed through a bag containing food, utensils, etc., to sterilise the contents.
-
Radiation (noun)
The shooting forth of anything from a point or surface, like diverging rays of light.
“heat radiation”
-
Radiation (noun)
The process of radiating waves or particles.
-
Radiation (noun)
The transfer of energy via radiation (as opposed to convection or conduction).
-
Radiation (noun)
Radioactive energy.