Main Difference
The main difference between Glucose and Fructose is that the Glucose is a simple sugar and Fructose is a chemical compound.
-
Glucose
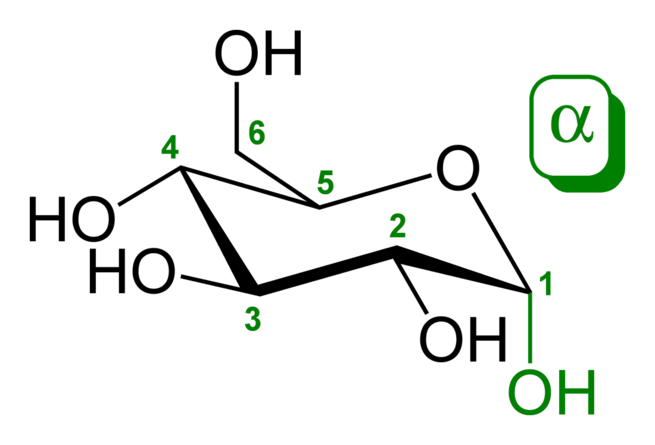
Glucose (also called dextrose) is a simple sugar with the molecular formula C6H12O6. Glucose is the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight. There it is used to make cellulose in cell walls, which is the most abundant carbohydrate. In energy metabolism, glucose is the most important source of energy in all organisms. Glucose for metabolism is partially stored as a polymer, in plants mainly as starch and amylopectin and in animals as glycogen. Glucose circulates in the blood of animals as blood sugar. The naturally occurring form of glucose is D-glucose, while L-glucose is produced synthetically in comparably small amounts and is of lesser importance.
Glucose, as intravenous sugar solution, is on the World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines, the most important medications needed in a basic health system. The name glucose derives through the French from the Greek γλυκός, which means “sweet,” in reference to must, the sweet, first press of grapes in the making of wine. The suffix “-ose” is a chemical classifier, denoting a sugar.
-
Fructose
Fructose, or fruit sugar, is a simple ketonic monosaccharide found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and galactose, that are absorbed directly into blood during digestion. Fructose was discovered by French chemist Augustin-Pierre Dubrunfaut in 1847. The name “fructose” was coined in 1857 by the English chemist William Allen Miller. Pure, dry fructose is a sweet, white, odorless, crystalline solid, and is the most water-soluble of all the sugars.
Fructose is found in honey, tree and vine fruits, flowers, berries, and most root vegetables.
Commercially, fructose is derived from sugar cane, sugar beets, and maize. Crystalline fructose is the monosaccharide, dried, ground, and of high purity. High-fructose corn syrup is a mixture of glucose and fructose as monosaccharides. Sucrose is a compound with one molecule of glucose covalently linked to one molecule of fructose. All forms of fructose, including fruits and juices, are commonly added to foods and drinks for palatability and taste enhancement, and for browning of some foods, such as baked goods. About 240,000 tonnes of crystalline fructose are produced annually.Excessive consumption of fructose may contribute to insulin resistance, obesity, elevated LDL cholesterol and triglycerides, leading to metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. The European Food Safety Authority stated that fructose is preferable over sucrose and glucose in sugar-sweetened foods and beverages because of its lower effect on postprandial blood sugar levels, and also noted that “high intakes of fructose may lead to metabolic complications such as dyslipidaemia, insulin resistance, and increased visceral adiposity”. Further, the UK’s Scientific Advisory Committee on Nutrition in 2015 disputed the claims of fructose causing metabolic disorders, stating that “there is insufficient evidence to demonstrate that fructose intake leads to adverse health outcomes independent of any effects related to its presence as a component of total and free sugars.”
-
Glucose (noun)
A simple cellular metabolism.
-
Fructose (noun)
A monosaccharide ketose sugar, formula C6H12O6.
-
Glucose (noun)
a simple sugar which is an important energy source in living organisms and is a component of many carbohydrates.
-
Glucose (noun)
a syrup containing glucose and other sugars, made by hydrolysis of starch and used in the food industry.
-
Fructose (noun)
a sugar of the hexose class found especially in honey and fruit.
