Main Difference
The main difference between Evolution and Adaptation is that the Evolution is a change in the inherited characteristics of biological populations over successive generations and Adaptation is a trait with a current functional role in the life history of an organism that is maintained and evolved by means of natural selection
-
Evolution
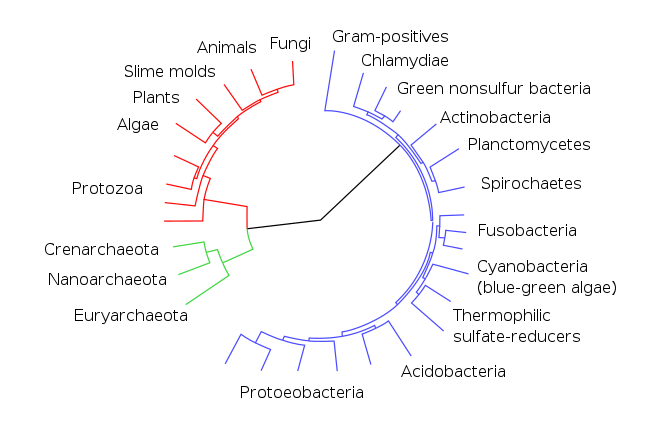
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. Evolutionary processes give rise to biodiversity at every level of biological organisation, including the levels of species, individual organisms, and molecules.
Repeated formation of new species (speciation), change within species (anagenesis), and loss of species (extinction) throughout the evolutionary history of life on Earth are demonstrated by shared sets of morphological and biochemical traits, including shared DNA sequences. These shared traits are more similar among species that share a more recent common ancestor, and can be used to reconstruct a biological “tree of life” based on evolutionary relationships (phylogenetics), using both existing species and fossils. The fossil record includes a progression from early biogenic graphite, to microbial mat fossils, to fossilised multicellular organisms. Existing patterns of biodiversity have been shaped both by speciation and by extinction.
In the mid-19th century, Charles Darwin formulated the scientific theory of evolution by natural selection, published in his book On the Origin of Species (1859). Evolution by natural selection is a process first demonstrated by the observation that often, more offspring are produced than can possibly survive. This is followed by three observable facts about living organisms: 1) traits vary among individuals with respect to morphology, physiology, and behaviour (phenotypic variation), 2) different traits confer different rates of survival and reproduction (differential fitness), and 3) traits can be passed from generation to generation (heritability of fitness). Thus, in successive generations members of a population are replaced by progeny of parents better adapted to survive and reproduce in the biophysical environment in which natural selection takes place.
This teleonomy is the quality whereby the process of natural selection creates and preserves traits that are seemingly fitted for the functional roles they perform. The processes by which the changes occur, from one generation to another, are called evolutionary processes or mechanisms. The four most widely recognised evolutionary processes are natural selection (including sexual selection), genetic drift, mutation and gene migration due to genetic admixture. Natural selection and genetic drift sort variation; mutation and gene migration create variation.
Consequences of selection can include meiotic drive (unequal transmission of certain alleles), nonrandom mating and genetic hitchhiking. In the early 20th century the modern evolutionary synthesis integrated classical genetics with Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection through the discipline of population genetics. The importance of natural selection as a cause of evolution was accepted into other branches of biology. Moreover, previously held notions about evolution, such as orthogenesis, evolutionism, and other beliefs about innate “progress” within the largest-scale trends in evolution, became obsolete. Scientists continue to study various aspects of evolutionary biology by forming and testing hypotheses, constructing mathematical models of theoretical biology and biological theories, using observational data, and performing experiments in both the field and the laboratory.
All life on Earth shares a common ancestor known as the last universal common ancestor (LUCA), which lived approximately 3.5–3.8 billion years ago. A December 2017 report stated that 3.45 billion-year-old Australian rocks once contained microorganisms, the earliest direct evidence of life on Earth. Nonetheless, this should not be assumed to be the first living organism on Earth; a study in 2015 found “remains of biotic life” from 4.1 billion years ago in ancient rocks in Western Australia. In July 2016, scientists reported identifying a set of 355 genes from the LUCA of all organisms living on Earth. More than 99 percent of all species that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates of Earth’s current species range from 10 to 14 million, of which about 1.9 million are estimated to have been named and 1.6 million documented in a central database to date. More recently, in May 2016, scientists reported that 1 trillion species are estimated to be on Earth currently with only one-thousandth of one percent described.
In terms of practical application, an understanding of evolution has been instrumental to developments in numerous scientific and industrial fields, including agriculture, human and veterinary medicine, and the life sciences in general. Discoveries in evolutionary biology have made a significant impact not just in the traditional branches of biology but also in other academic disciplines, including biological anthropology, and evolutionary psychology. Evolutionary computation, a sub-field of artificial intelligence, involves the application of Darwinian principles to problems in computer science.
-
Adaptation
In biology, adaptation has three related meanings. Firstly, it is the dynamic evolutionary process that fits organisms to their environment, enhancing their evolutionary fitness. Secondly, it is a state reached by the population during that process. Thirdly, it is a phenotypic or adaptive trait, with a functional role in each individual organism, that is maintained and has been evolved by natural selection.
Organisms face a succession of environmental challenges as they grow, and show adaptive plasticity as traits develop in response to the imposed conditions. This gives them resilience to varying environments.
-
Evolution (noun)
The process of accumulating change.
“Among other forms of change, the evolution of transportation has involved modification, diversification, convergence, divergence, hybridization, differentiation, and naturally, selection.”
-
Evolution (noun)
A progression of change, often branching and diversifying in the process.
“The ongoing evolution of Lolita subculture fashion includes, among other things, the ballet style.”
-
Evolution (noun)
Gradual directional change especially one leading to a more advanced or complex form; growth; development.
“The evolution of the universe began with a bang.”
-
Evolution (noun)
The change in the genetic composition of a population over successive generations.
-
Evolution (noun)
The act or an instance of giving off gas; emission.
-
Evolution (noun)
The extraction of a root from a quantity.
-
Evolution (noun)
One of a series of ordered movements.
-
Evolution (noun)
A turning movement of the body.
-
Adaptation (noun)
The process of adapting something or becoming adapted to a situation; adjustment, modification.
-
Adaptation (noun)
A change that is made or undergone to suit a condition or environment.
-
Adaptation (noun)
The process of change that an organism undergoes to be better suited to its environment.
“maladaptation”
-
Adaptation (noun)
An instance of an organism undergoing change, or the structure or behavior that is changed.
-
Adaptation (noun)
The process of adapting an artistic work from a different medium.
-
Adaptation (noun)
An artistic work that has been adapted from a different medium.
-
Evolution (noun)
the process by which different kinds of living organism are believed to have developed from earlier forms during the history of the earth.
-
Evolution (noun)
the gradual development of something
“the forms of written languages undergo constant evolution”
-
Evolution (noun)
the giving off of a gaseous product, or of heat
“the evolution of oxygen occurs rapidly in this process”
-
Evolution (noun)
a pattern of movements or manoeuvres
“flocks of waders often perform aerial evolutions”
-
Evolution (noun)
the extraction of a root from a given quantity.