-
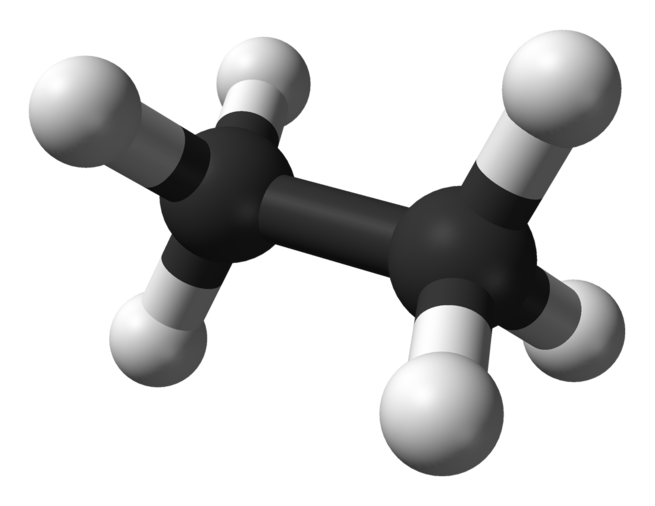
Ethane
Ethane ( or ) is an organic chemical compound with chemical formula C2H6. At standard temperature and pressure, ethane is a colorless, odorless gas. Like many hydrocarbons, ethane is isolated on an industrial scale from natural gas and as a petrochemical by-product of petroleum refining. Its chief use is as feedstock for ethylene production.
Related compounds may be formed by replacing a hydrogen atom with another functional group; the ethane moiety is called an ethyl group. For example, an ethyl group linked to a hydroxyl group yields ethanol, the alcohol in beverages.
-
Ethylene
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula C2H4 or H2C=CH2. It is a colorless flammable gas with a faint “sweet and musky” odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon-carbon double bonds).
Ethylene is widely used in the chemical industry, and its worldwide production (over 150 million tonnes in 2016) exceeds that of any other organic compound. Much of this production goes toward polyethylene, a widely used plastic containing polymer chains of ethylene units in various chain lengths. Ethylene is also an important natural plant hormone, and is used in agriculture to force the ripening of fruits. Ethylene’s hydrate is ethanol.
-
Ethane (noun)
An aliphatic hydrocarbon, C2H6, gaseous at normal temperatures and pressures, being a constituent of natural gas.
-
Ethane (noun)
The same compound, subjected to modification by replacing one or more of the hydrogen atoms with other radicals.
“chlorinated ethanes; halogenated ethanes”
-
Ethylene (noun)
The common name for the organic chemical compound ethene. The simplest alkene, a colorless gaseous (at room temperature and pressure) hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C2H4.
-
Ethylene (noun)
The divalent radical derived from ethane.
-
Ethane (noun)
a colourless, odourless, flammable gas which is a constituent of petroleum and natural gas. It is the second member of the alkane series.