Main Difference
The main difference between Epidermis and Epithelium is that the Epidermis is a outermost layers of the skin and Epithelium is a type of animal tissue
-
Epidermis
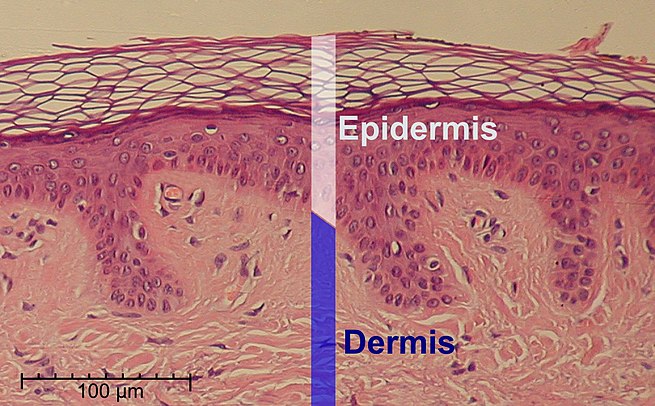
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that make up the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water released from the body into the atmosphere through transepidermal water loss. The epidermis is composed of multiple layers of flattened cells that overlie a base layer (stratum basale) composed of columnar cells arranged perpendicularly.
The rows of cells develop from stem cells in the basal layer. Cellular mechanisms for regulating water and sodium levels (ENaCs) are found in all layers of the epidermis.The word epidermis is derived through Latin from Ancient Greek epidermis, itself from Ancient Greek epi, meaning ‘over, upon’ and from Ancient Greek derma, meaning ‘skin’. Something related to or part of the epidermis is termed epidermal.
The human epidermis is a familiar example of epithelium, particularly a stratified squamous epithelium.
-
Epithelium
Epithelium () is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin.
There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous, columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a single layer of cells as simple epithelium, either squamous, columnar, cuboidal, pseudo-stratified columnar or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. All glands are made up of epithelial cells. Functions of epithelial cells include secretion, selective absorption, protection, transcellular transport, and sensing.
Epithelial layers contain no blood vessels, so they must receive nourishment via diffusion of substances from the underlying connective tissue, through the basement membrane. Cell junctions are well-employed in epithelial tissues.
-
Epidermis (noun)
The outer, protective layer of the skin of vertebrates, covering the dermis
-
Epidermis (noun)
The similar outer layer of cells in invertebrates and plants
-
Epithelium (noun)
A membranous tissue composed of one or more layers of cells which forms the covering of most internal and external surfaces of the body and its organs: internally including the lining of vessels and other small cavities, and externally being the skin.
“epithelial tissue”
