Main Difference
The main difference between Effusion and Edema is that the Effusion is a process of a gas escaping through a small hole and Edema is a abnormal accumulation of fluid in the interstitium.
-
Effusion
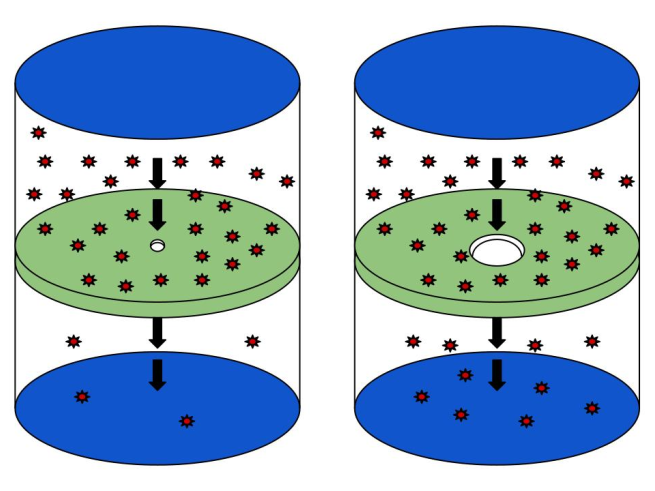
In physics and chemistry, effusion is the process in which a gas escapes through a hole of diameter considerably smaller than the mean free path of the molecules. Under these conditions, essentially all molecules which arrive at the hole continue and pass through the hole, since collisions between molecules in the region of the hole are negligible. Conversely, when the diameter is larger than the mean free path of the gas, flow obeys the Sampson flow law.
In medical terminology, an effusion refers to accumulation of fluid in an anatomic space, usually without loculation. Specific examples include subdural, mastoid, pericardial and pleural effusions.
-
Edema
Edema, also spelled oedema or œdema, is an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the interstitium, located beneath the skin and in the cavities of the body, which can cause severe pain. Clinically, edema manifests as swelling. The amount of interstitial fluid is determined by the balance of fluid homeostasis; and the increased secretion of fluid into the interstitium. The word is from Greek οἴδημα oídēma meaning “swelling”. The condition is also known (mostly archaic) as dropsy.
-
Effusion (noun)
A liquid outpouring.
-
Effusion (noun)
Process of gases passing through a hole or holes considerably smaller than the mean free path of the gas molecules.
-
Effusion (noun)
An outpouring of speech or emotion.
-
Effusion (noun)
the seeping of fluid into a body cavity; the fluid itself.
-
Edema (noun)
An excessive accumulation of serum in tissue spaces or a body cavity.
-
Edema (noun)
A similar swelling in plants caused by excessive accumulation of water.