Main Difference
The main difference between Dystrophy and Atrophy is that the Dystrophy is a Wikipedia disambiguation page and Atrophy is a partial or complete wasting away of a part of the body.
-
Dystrophy
Dystrophy is the degeneration of tissue, due to disease or malnutrition, most likely due to heredity.
-
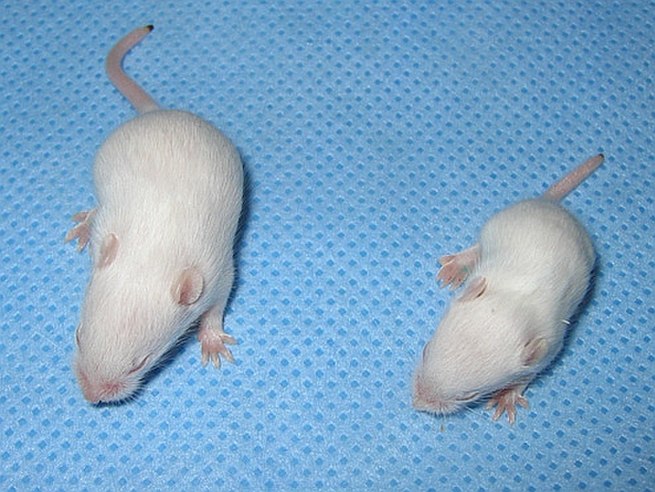
Atrophy
Atrophy is the partial or complete wasting away of a part of the body. Causes of atrophy include mutations (which can destroy the gene to build up the organ), poor nourishment, poor circulation, loss of hormonal support, loss of nerve supply to the target organ, excessive amount of apoptosis of cells, and disuse or lack of exercise or disease intrinsic to the tissue itself. In medical practice, hormonal and nerve inputs that maintain an organ or body part are said to have trophic effects. A diminished muscular trophic condition is designated as atrophy. Atrophy is reduction in size of cell, organ or tissue, after attaining its normal maturured growth. However, hypoplasia is reduction of size which has not attained at all to normal maturity.
Atrophy is the general physiological process of reabsorption and breakdown of tissues, involving apoptosis. When it occurs as a result of disease or loss of trophic support due to other disease, it is termed pathological atrophy, although it can be a part of normal body development and homeostasis as well.
-
Dystrophy (noun)
A wasting of body tissues, of genetic origin or due to inadequate or defective nutrition.
-
Atrophy (noun)
A reduction in the functionality of an organ caused by disease, injury or lack of use. from early 17th c.
-
Atrophy (verb)
To wither or waste away. from early 18th c.
-
Atrophy (verb)
To cause to waste away or become abortive; to starve or weaken.
