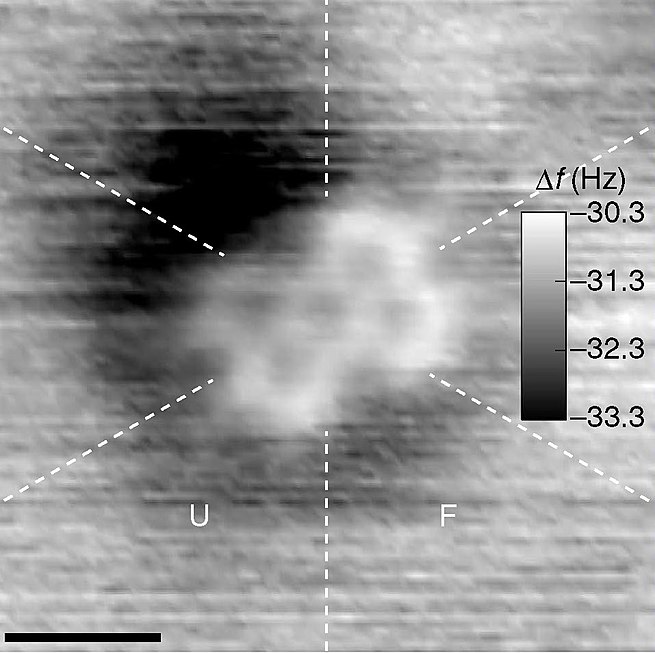
-
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their lack of electrical charge. However, in quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the term molecule is often used less strictly, also being applied to polyatomic ions.
In the kinetic theory of gases, the term molecule is often used for any gaseous particle regardless of its composition. According to this definition, noble gas atoms are considered molecules as they are monatomic molecules.A molecule may be homonuclear, that is, it consists of atoms of one chemical element, as with oxygen (O2); or it may be heteronuclear, a chemical compound composed of more than one element, as with water (H2O). Atoms and complexes connected by non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen bonds or ionic bonds, are typically not considered single molecules.Molecules as components of matter are common in organic substances (and therefore biochemistry). They also make up most of the oceans and atmosphere. However, the majority of familiar solid substances on Earth, including most of the minerals that make up the crust, mantle, and core of the Earth, contain many chemical bonds, but are not made of identifiable molecules. Also, no typical molecule can be defined for ionic crystals (salts) and covalent crystals (network solids), although these are often composed of repeating unit cells that extend either in a plane (such as in graphene) or three-dimensionally (such as in diamond, quartz, or sodium chloride). The theme of repeated unit-cellular-structure also holds for most condensed phases with metallic bonding, which means that solid metals are also not made of molecules. In glasses (solids that exist in a vitreous disordered state), atoms may also be held together by chemical bonds with no presence of any definable molecule, nor any of the regularity of repeating units that characterizes crystals.
-
Compound (noun)
an enclosure within which workers, prisoners, or soldiers are confined
-
Compound (noun)
a group of buildings situated close together, e.g. for a school or block of offices
-
Compound (noun)
Anything made by combining several things.
-
Compound (noun)
A substance made from any combination elements.
-
Compound (noun)
A substance formed by chemical union of two or more ingredients in definite proportions by weight.
-
Compound (noun)
A lexeme that consists of more than one stem; compound word; for example laptop, formed from lap and top.
-
Compound (noun)
a compound locomotive, a steam locomotive with both high-pressure and low-pressure cylinders.
-
Compound (adjective)
composed of elements; not simple
“a compound word”
-
Compound (adjective)
dealing with numbers of various denominations of quantity, or with processes more complex than the simple process
“compound addition; compound proportion”
-
Compound (adjective)
An octave higher than originally (i.e. a compound major second is equivalent to a major ninth).
-
Compound (verb)
To form (a resulting mixture) by combining different elements, ingredients, or parts.
“to compound a medicine”
-
Compound (verb)
To assemble (ingredients) into a whole; to combine, mix, or unite.
-
Compound (verb)
To modify or change by combination with some other thing or part; to mingle with something else.
-
Compound (verb)
To settle by agreeing on less than the claim, or on different terms than those stipulated.
“to compound a debt”
-
Compound (verb)
To settle amicably; to adjust by agreement; to compromise.
-
Compound (verb)
To come to terms of agreement; to agree; to settle by a compromise; usually followed by with before the person participating, and for before the thing compounded or the consideration.
-
Compound (verb)
To compose; to constitute.
-
Compound (verb)
To increase in value with interest, where the interest is earned on both the principal sum and prior earned interest.
-
Compound (verb)
To worsen a situation
-
Molecule (noun)
The smallest particle of a specific element or compound that retains the chemical properties of that element or compound; two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds.
“Hydrogen chloride is a diatomic molecule, consisting of a hydrogen atom and a chlorine atom.”
-
Molecule (noun)
A tiny amount.
