Main Difference
The main difference between Apoplast and Symplast is that the The cell membranes and intracellular regions in a plant are connected through plasmodesmata and plants may be described as having 2 major compartments: the living symplast and the non-living apoplast. The apoplast is external to the plasma membrane and Symplast is a The interconnected cell membranes and intracellular regions of a plant. The interconnections occur via the plasmodesmata
-
Apoplast
Inside a plant, the apoplast is the space outside the plasma membrane within which material can diffuse freely. It is interrupted by the Casparian strip in roots, by air spaces between plant cells and by the plant cuticle.
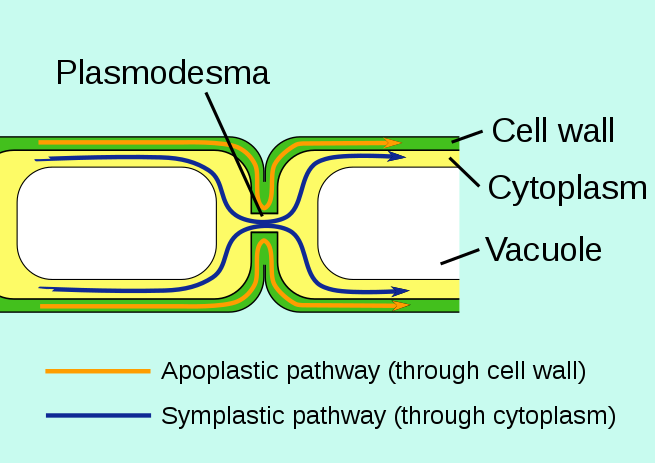
Structurally, the apoplast is formed by the continuum of cell walls of adjacent cells as well as the extracellular spaces, forming a tissue level compartment comparable to the symplast. The apoplastic route facilitates the transport of water and solutes across a tissue or organ. This process is known as apoplastic transport.
The apoplast is important for all the plant’s interaction with its environment. The main carbon source (carbon dioxide) needs to be solubilized in the apoplast before it diffuses through the plasma membrane into the cell’s cytoplasm (symplast) and is used by the chloroplasts during photosynthesis. In the roots, ions diffuse into the apoplast of the epidermis before diffusing into the symplast, or in some cases being taken up by specific ion channels, and being pulled by the plant’s transpiration stream, which also occurs completely within the boundaries of the apoplast. Similarly, all gaseous molecules emitted and received by plants such as plant hormones and other pheromones must pass the apoplast. In nitrate poor soils, acidification of the apoplast increases cell wall extensibility and root growth rate. This is believed to be caused by a decrease in nitrate uptake (due to deficit in the soil medium) and supplanted with an increase in chloride uptake. H+ATPase increases the efflux of H+, thus acidifying the apoplast. The apoplast is also a site for cell-to-cell communication. During local oxidative stress, hydrogen peroxide and superoxide anions can diffuse through the apoplast and transport a warning signal to neighbouring cells. In addition, a local alkalinization of the apoplast due to such a stress can travel within minutes to the rest of the plant body via the xylem and trigger systemic acquired resistance.
The apoplast also plays an important role in resistance to aluminium toxicity and resistance. In addition to resistance to chemicals, the apoplast provides the rich environment for microorganisms endophytes which arises the abiotic resistance of plants. Exclusion of aluminium ions in the apoplast prevent toxic levels which inhibit shoot growth, reducing crop yields
-
Symplast
The symplast of a plant is the inner side of the plasma membrane in which water and low-molecular-weight solutes can freely diffuse. Symplast cells have more than one nucleus.
Or, The connection made between cells by the cytoplasmic connection of plasmodesmata is called symplast
(Water and low molecular weight pass through pore in the adjacent cell walls)And cytoplasmic connection through pore are known as plasmodesmata..
The plasmodesmata allow the direct flow of small molecules such as sugars, amino acids, and ions between cells. Larger molecules, including transcription factors and plant viruses, can also be transported through with the help of actin structures.
This allows direct cytoplasm-to-cytoplasm flow of water and other nutrients along concentration gradients. In particular, symplastic flow is used in the root systems to bring in nutrients from soil. It moves these solutes from epidermis cells through the cortex into the endodermis. Once solutes reach the endodermal cells through apoplastic flow, they are forced into the symplastic pathway due to the presence of the Casparian strip. Once the solutes are passively filtered, they eventually reach the pericycle, where it can be moved into the xylem for long distance transport.
It is contrasted with the apoplastic flow, which uses cell wall transport.
-
Apoplast (noun)
The space outside of a plant’s plasma membrane through which water and soluble nutrients are transported across a tissue or organ
-
Symplast (noun)
The inner side of the plasma membrane of a plant in which water can freely diffuse.