-
Polypropylene
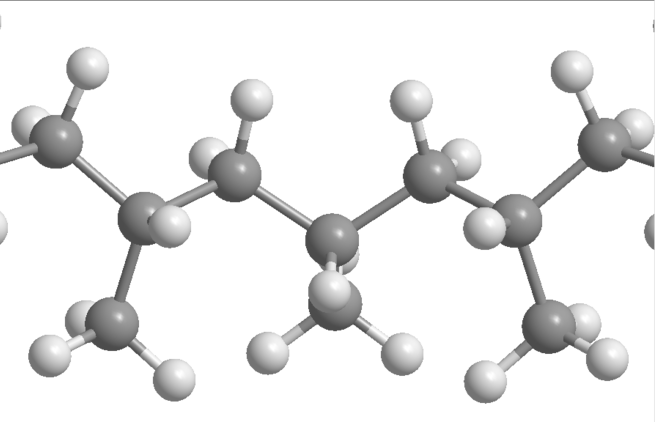
Polypropylene (PP), also known as polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications. It is produced via chain-growth polymerization from the monomer propylene.
Polypropylene belongs to the group of polyolefins and is partially crystalline and non-polar. Its properties are similar to polyethylene, but it is slightly harder and more heat resistant. It is a white, mechanically rugged material and has a high chemical resistance. Polypropylene is the second-most widely produced commodity plastic (after polyethylene) and it is often used in packaging and labeling. In 2013, the global market for polypropylene was about 55 million tonnes.
-
Polyallomer (noun)
A copolymer of more than one olefin, especially of propylene and another olefin
-
Polypropylene (noun)
A thermoplastic resin made by the polymerization of propylene, and used for films, fibres, or moulding materials. Also known as polypropene.
-
Polyallomer (noun)
Any of a class of crystalline thermoplastics which are copolymers of two or more different alkenes, especially ethylene and propylene.
-
Polypropylene (noun)
a synthetic resin which is a polymer of propylene, used chiefly for films, fibres, or moulding materials
“high-impact polypropylene”
“polypropylene underwear”