-
Phosphate
A phosphate is a chemical derivative of phosphoric acid. The phosphate ion (PO3−4) is an inorganic chemical, the conjugate base that can form many different salts. In organic chemistry, a phosphate, or organophosphate, is an ester of phosphoric acid. Of the various phosphoric acids and phosphates, organic phosphates are important in biochemistry and biogeochemistry (and, consequently, in ecology), and inorganic phosphates are mined to obtain phosphorus for use in agriculture and industry. At elevated temperatures in the solid state, phosphates can condense to form pyrophosphates.
In biology, adding phosphates to—and removing them from—proteins in cells are both pivotal in the regulation of metabolic processes. Referred to as phosphorylation and dephosphorylation, respectively, they are important ways that energy is stored and released in living systems.
-
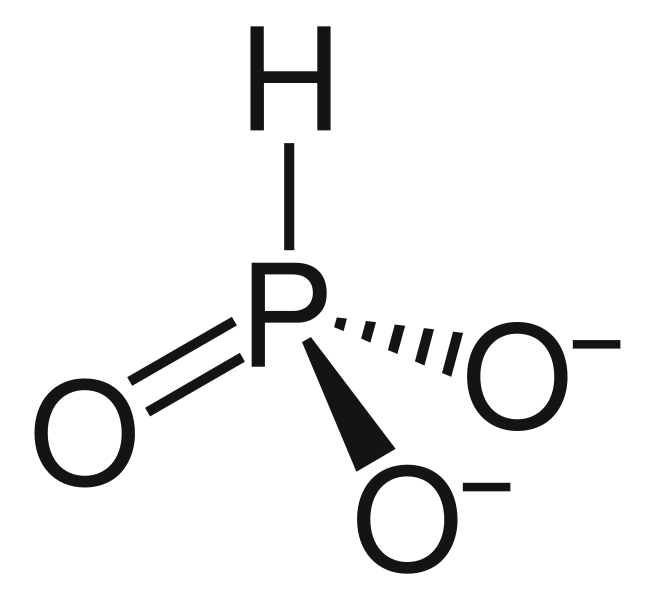
Phosphite (noun)
any salt or ester of phosphorous acid
-
Phosphite (noun)
the anion PO33-, or the trivalent radical PO3
-
Phosphate (noun)
Any salt or ester of phosphoric acid.
-
Phosphate (noun)
A carbonated soft drink sweetened with fruit syrup and with some phosphoric acid.
-
Phosphate (verb)
To treat or coat with a phosphate or with phosphoric acid
-
Phosphite (noun)
old-fashioned term for phosphonate
-
Phosphate (noun)
a salt or ester of phosphoric acid, containing PO₄³⁻ or a related anion or a group such as —OPO(OH)₂.
-
Phosphate (noun)
an effervescent soft drink containing phosphoric acid, soda water, and flavouring.
