Main Difference
The main difference between Pharynx and Larynx is that the Pharynx is a part of the throat that is behind the mouth and nasal cavity and Larynx is a voice box, an organ in the neck of amphibians, reptiles, and mammals.
-
Pharynx
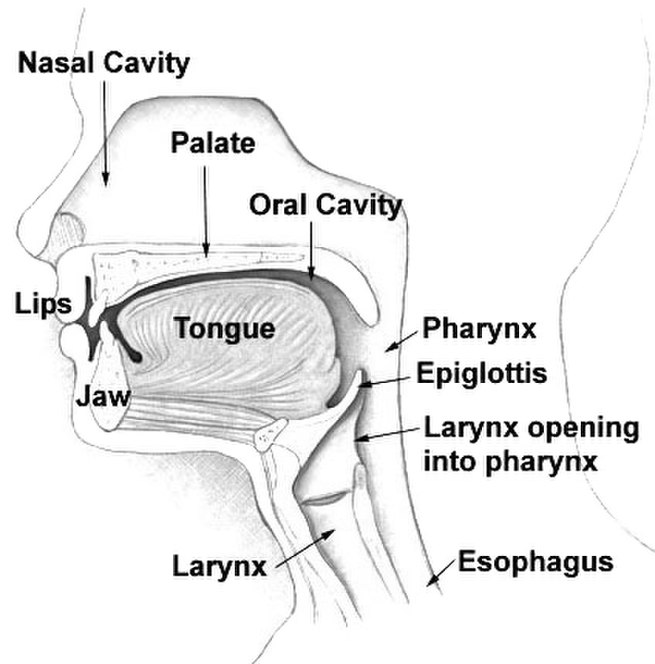
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat that is behind the mouth and nasal cavity and above the esophagus and the larynx, or the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs. The pharynx is an area found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though the structure is not universally the same across all of those species.
In humans the pharynx is part of the digestive system and also of the conducting zone of the respiratory system. (The conducting zone also includes the nostrils of the nose, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles, and their function is to filter, warm, and moisten air and conduct it into the lungs.) The pharynx makes up the part of the throat situated immediately behind the nasal cavity, behind the mouth and above the esophagus and larynx. The human pharynx is conventionally divided into three sections: the nasopharynx, the oropharynx and the laryngopharynx. It is also important in vocalization.
In humans there are two sets of pharyngeal muscles that form the pharynx, determining the shape of its lumen. These are arranged as an inner layer of longitudinal muscles and an outer circular layer.
-
Larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck of tetrapods involved in breathing, producing sound, and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The larynx houses the vocal folds, and manipulates pitch and volume, which is essential for phonation. It is situated just below where the tract of the pharynx splits into the trachea and the esophagus. The word larynx (plural larynges) comes from a similar Ancient Greek word (λάρυγξ lárynx).
-
Pharynx (noun)
The part of the alimentary canal and respiratory tract that extends from the back of the mouth and nasal cavity to the larynx and esophagus.
-
Larynx (noun)
An organ of the neck of mammals involved in breath control, protection of the trachea and sound production, housing the vocal cords, and that is situated at the point where the upper tract splits into the trachea and the oesophagus/esophagus.
