Main Difference
The main difference between Phagocytosis and Pinocytosis is that the Phagocytosis is a An endocytosis process that results in the engulfment of external particulate material by phagocytes. The particles are initially contained within phagocytic vacuoles (phagosomes), which then fuse with primary lysosomes to effect digestion of the par and Pinocytosis is a endocytosis process that results in the uptake of liquid material by cells from their external environment; literally ‘cell drinking’. Liquid is enclosed in vesicles, called pinosomes, formed by invagination of the plasma membrane
-
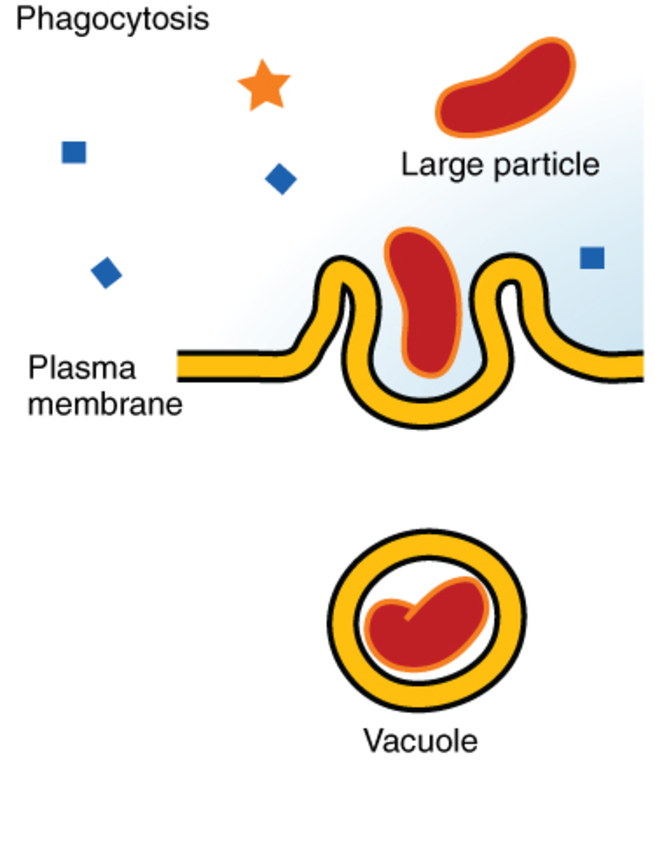
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis (from Ancient Greek φαγεῖν (phagein) ‘to eat’, and κύτος, (kytos) ‘cell’) is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is called a phagocyte.
In a multicellular organism’s immune system, phagocytosis is a major mechanism used to remove pathogens and cell debris. The ingested material is then digested in the phagosome. Bacteria, dead tissue cells, and small mineral particles are all examples of objects that may be phagocytized. Some protozoa use phagocytosis as means to obtain nutrients.
-
Pinocytosis
In cellular biology, pinocytosis, otherwise known as fluid endocytosis and bulk-phase pinocytosis, is a mode of endocytosis in which small particles suspended in extracellular fluid are brought into the cell through an invagination of the cell membrane, resulting in a suspension of the particles within a small vesicle inside the cell. These pinocytotic vesicles then typically fuse with early endosomes to hydrolyze (break down) the particles.
Pinocytosis is further segregated into the pathways macropinocytosis, clathrin-mediated endocytosis, caveolin-mediated endocytosis, or clathrin- and caveolin-independent endocytosis, all of which differ by the mechanism of vesicle formation as well as the resulting size of these vesicles.
Pinocytosis is variably subdivided into categories depending on molecular mechanism and the fate of the internalized molecules. Pinocytosis is, in some cases, considered to be a constitutive process, while in others it is receptor-mediated and highly regulated.
-
Phagocytosis (noun)
A form of endocytosis in which a cell incorporates a particle by extending pseudopodia and drawing the particle into a vacuole of its cytoplasm.
-
Pinocytosis (noun)
A form of endocytosis in which material enters a cell through its membrane and is incorporated in vesicles for digestion.
