-
Osmosis
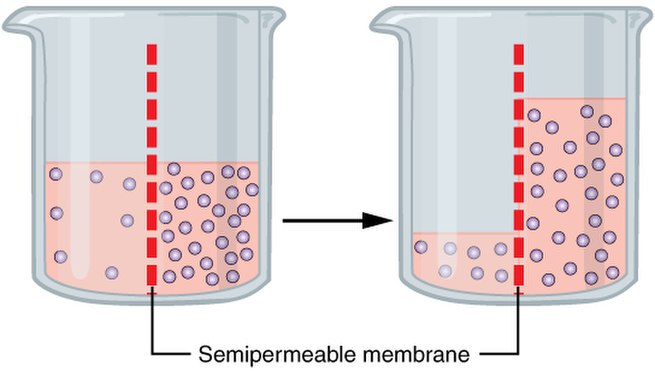
Osmosis () is the spontaneous net movement of solvent molecules through a selectively permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration, in the direction that tends to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides. It may also be used to describe a physical process in which any solvent moves across a selectively permeable membrane (permeable to the solvent, but not the solute) separating two solutions of different concentrations. Osmosis can be made to do work. Osmotic pressure is defined as the external pressure required to be applied so that there is no net movement of solvent across the membrane. Osmotic pressure is a colligative property, meaning that the osmotic pressure depends on the molar concentration of the solute but not on its identity.
Osmosis is a vital process in biological systems, as biological membranes are semipermeable. In general, these membranes are impermeable to large and polar molecules, such as ions, proteins, and polysaccharides, while being permeable to non-polar or hydrophobic molecules like lipids as well as to small molecules like oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and nitric oxide. Permeability depends on solubility, charge, or chemistry, as well as solute size. Water molecules travel through the plasma membrane, tonoplast membrane (vacuole) or protoplast by diffusing across the phospholipid bilayer via aquaporins (small transmembrane proteins similar to those responsible for facilitated diffusion and ion channels). Osmosis provides the primary means by which water is transported into and out of cells. The turgor pressure of a cell is largely maintained by osmosis across the cell membrane between the cell interior and its relatively hypotonic environment.
-
Reverse Osmosis
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a water purification process that uses a partially permeable membrane to separate ions, unwanted molecules and larger particles from drinking water. In reverse osmosis, an applied pressure is used to overcome osmotic pressure, a colligative property that is driven by chemical potential differences of the solvent, a thermodynamic parameter. Reverse osmosis can remove many types of dissolved and suspended chemical species as well as biological ones (principally bacteria) from water, and is used in both industrial processes and the production of potable water. The result is that the solute is retained on the pressurized side of the membrane and the pure solvent is allowed to pass to the other side. To be “selective”, this membrane should not allow large molecules or ions through the pores (holes), but should allow smaller components of the solution (such as solvent molecules, i.e., water, H2O) to pass freely.In the normal osmosis process, the solvent naturally moves from an area of low solute concentration (high water potential), through a membrane, to an area of high solute concentration (low water potential). The driving force for the movement of the solvent is the reduction in the Gibbs free energy of the system when the difference in solvent concentration on either side of a membrane is reduced, generating osmotic pressure due to the solvent moving into the more concentrated solution. Applying an external pressure to reverse the natural flow of pure solvent, thus, is reverse osmosis. The process is similar to other membrane technology applications.
Reverse osmosis differs from filtration in that the mechanism of fluid flow is by osmosis across a membrane. The predominant removal mechanism in membrane filtration is straining, or size exclusion, where the pores are 0.01 micrometers or larger, so the process can theoretically achieve perfect efficiency regardless of parameters such as the solution’s pressure and concentration. Reverse osmosis instead involves solvent diffusion across a membrane that is either nonporous or uses nanofiltration with pores 0.001 micrometers in size. The predominant removal mechanism is from differences in solubility or diffusivity, and the process is dependent on pressure, solute concentration, and other conditions. Reverse osmosis is most commonly known for its use in drinking water purification from seawater, removing the salt and other effluent materials from the water molecules.
-
Osmosis (noun)
The net movement of solvent molecules, usually water, from a region of lower solute concentration to a region of higher solute concentration through a partially permeable membrane.
-
Osmosis (noun)
Picking up knowledge accidentally, without actually seeking that particular knowledge.
“I was reading about chickens, and I guess I learned about hawks through osmosis.”
