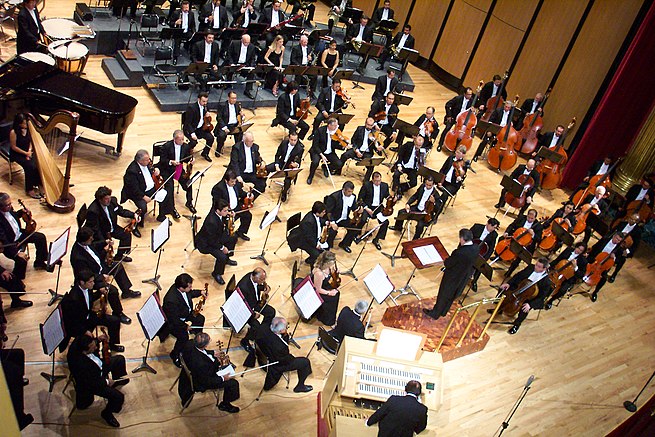
-
Orchestra
An orchestra (; Italian: [orˈkɛstra]) is a large instrumental ensemble typical of classical music, which combines instruments from different families, including bowed string instruments such as the violin, viola, cello, and double bass, brass instruments such as the horn, trumpet, trombone and tuba, woodwinds such as the flute, oboe, clarinet and bassoon, and percussion instruments such as the timpani, bass drum, triangle, snare drum, cymbals, and mallet percussion instruments each grouped in sections. Other instruments such as the piano and celesta may sometimes appear in a fifth keyboard section or may stand alone, as may the concert harp and, for performances of some modern compositions, electronic instruments.
A full-size Western orchestra may sometimes be called a symphony orchestra or philharmonic orchestra (phil-, Greek for “loving” + “harmonic”). The actual number of musicians employed in a given performance may vary from seventy to over one hundred musicians, depending on the work being played and the size of the venue. A chamber orchestra (sometimes concert orchestra) is a smaller-sized ensemble of about fifty musicians or fewer. Orchestras that specialize in the Baroque music of, for example, Johann Sebastian Bach and George Frideric Handel, or Classical repertoire, such as that of Haydn and Mozart, tend to be smaller than orchestras performing a Romantic music repertoire, such as the symphonies of Johannes Brahms. The typical orchestra grew in size throughout the 18th and 19th centuries, reaching a peak with the large orchestras (of as many as 120 players) called for in the works of Richard Wagner, and later, Gustav Mahler.
Orchestras are usually led by a conductor who directs the performance with movements of the hands and arms, often made easier for the musicians to see by use of a conductor’s baton. The conductor unifies the orchestra, sets the tempo and shapes the sound of the ensemble. The conductor also prepares the orchestra by leading rehearsals before the public concert, in which the conductor provides instructions to the musicians on their interpretation of the music being performed.
The leader of the first violin section, commonly called the concertmaster, also plays an important role in leading the musicians. In the Baroque music era (1600–1750), orchestras were often led by the concertmaster or by a chord-playing musician performing the basso continuo parts on a harpsichord or pipe organ, a tradition that some 20th-century and 21st-century early music ensembles continue. Orchestras play a wide range of repertoire, including symphonies, opera and ballet overtures, concertos for solo instruments, and as pit ensembles for operas, ballets, and some types of musical theatre (e.g., Gilbert and Sullivan operettas).
Amateur orchestras include those made up of students from an elementary school or a high school, youth orchestras, and community orchestras; the latter two typically being made up of amateur musicians from a particular city or region.
The term orchestra derives from the Greek ὀρχήστρα (orchestra), the name for the area in front of a stage in ancient Greek theatre reserved for the Greek chorus.
-
Orchestra (noun)
A large group of musicians who play together on various instruments, usually including some from strings, woodwind, brass and/or percussion; the instruments played by such a group.
-
Orchestra (noun)
A semicircular space in front of the stage used by the chorus in Ancient Greek and Hellenistic theatres.
-
Orchestra (noun)
The area in a theatre or concert hall where the musicians sit, immediately in front of and below the stage, sometimes (also) used by other performers.
-
Band (noun)
A strip of material used for strengthening or coupling.
-
Band (noun)
A strip of material wrapped around things to hold them together.
-
Band (noun)
A narrow strip of cloth or other material on clothing, to bind, strengthen, or ornament it.
-
Band (noun)
A strip along the spine of a book where the pages are attached.
-
Band (noun)
A long strip of material, color, etc, that is different from the surrounding area.
“sandstone with bands of shale”
-
Band (noun)
A strip of decoration.
-
Band (noun)
A belt or strap that is part of a machine.
-
Band (noun)
A continuous tablet, stripe, or series of ornaments, as of carved foliage, of colour, or of brickwork.
-
Band (noun)
That which serves as the means of union or connection between persons; a tie.
-
Band (noun)
A linen collar or ruff worn in the 16th and 17th centuries.
-
Band (noun)
Two strips of linen hanging from the neck in front as part of a clerical, legal, or academic dress.
-
Band (noun)
A part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
-
Band (noun)
A group of energy levels in a solid state material.
“valence band;”
“conduction band”
-
Band (noun)
A bond.
-
Band (noun)
Pledge; security.
-
Band (noun)
A ring, such as a wedding ring (wedding band), or a ring put on a bird’s leg to identify it.
-
Band (noun)
Any distinguishing line formed by chromatography, electrophoresis etc
-
Band (noun)
A wad of money totaling $10K, held together by a band; money
-
Band (noun)
A group of musicians who perform together as an ensemble, usually for a professional recording artist.
-
Band (noun)
A type of orchestra originally playing janissary music.
-
Band (noun)
A marching band.
-
Band (noun)
A group of people loosely united for a common purpose a band of thieves.
-
Band (noun)
A small group of people living in a simple society.
-
Band (noun)
A group of aboriginals that has official recognition as an organized unit by the federal government of Canada.
-
Band (verb)
To fasten with a band.
-
Band (verb)
To fasten an identifying band around the leg of (a bird).
-
Band (verb)
To group together for a common purpose; to confederate.
