-
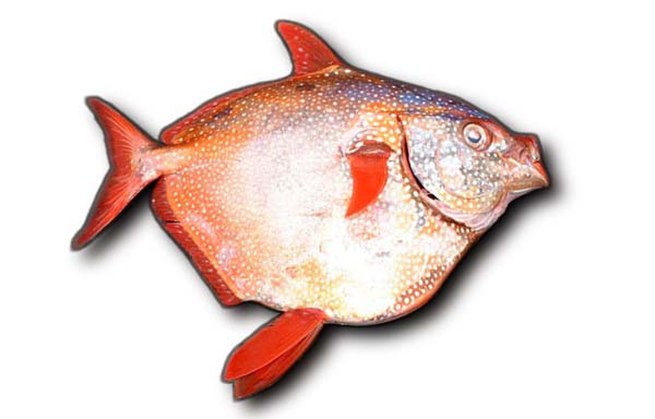
Opah
Opahs (also commonly known as moonfish, sunfish (not to be confused with Molidae), kingfish, redfin ocean pan, and Jerusalem haddock) are large, colorful, deep-bodied pelagic lampriform fishes comprising the small family Lampridae (also spelled Lamprididae).
In 2015 the Opah was discovered to have near whole body endothermy, a form of regional endothermy. This is different from “warm blooded” in the sense of birds and mammals and is not the first fish discovered with this ability. It may be the most completely endothermic fish.Other species of fish also possess this ability, such as tuna and some sharks. Only two living species occur in a single genus: Lampris (from the Greek lamprid-, “brilliant” or “clear”). One species is found in tropical to temperate waters of most oceans, while the other is limited to a circumglobal distribution in the Southern Ocean, with the 34th parallel south as its northern limit. Two additional species, one in the genus Lampris and the other in the monotypic Megalampris, are only known from fossil remains. The extinct family, Turkmenidae, from the Paleogene of Central Asia, is closely related, though much smaller.
-
Opah (noun)
Any of various large, colourful, deep-bodied pelagic fish of the family Lamprididae.
-
Sunfish (noun)
Any of various small freshwater fishes of the family Centrarchidae, often with iridescent colours and having a laterally compressed body.
-
Sunfish (noun)
Any of various large marine fishes of the family Molidae that have an oval compressed body.
