Main Difference
The main difference between Monosaccharide and Polysaccharide is that the Monosaccharide is a simple sugars such as glucose and fructose and Polysaccharide is a polymeric carbohydrate molecules composed of long chains of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages and on hydrolysis give the constituent monosaccharides or oligosaccharides
-
Monosaccharide
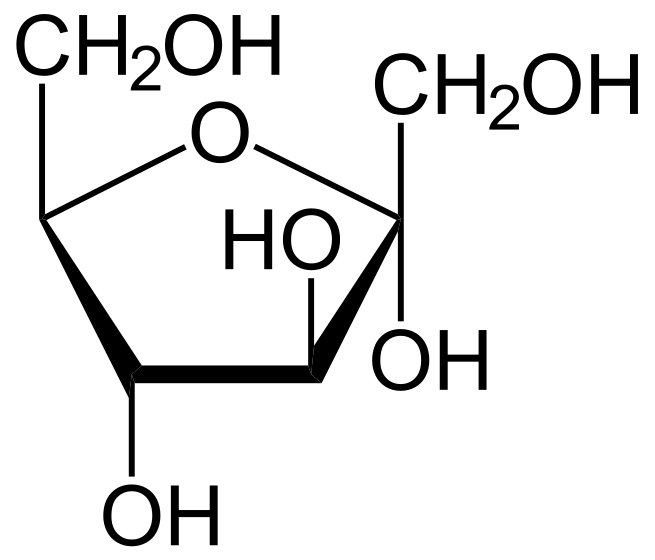
Monosaccharides (from Greek monos: single, sacchar: sugar), also called simple sugars, are the most basic units of carbohydrates. They are fundamental units of carbohydrates and cannot be further hydrolyzed to simpler compounds. The general formula is CnH2nOn. They are the simplest form of sugar and are usually colorless, water-soluble, and crystalline solids. Some monosaccharides have a sweet taste. Examples of monosaccharides include glucose (dextrose), fructose (levulose) and galactose. Monosaccharides are the building blocks of disaccharides (such as sucrose and lactose) and polysaccharides (such as cellulose and starch). Further, each carbon atom that supports a hydroxyl group (so, all of the carbons except for the primary and terminal carbon) is chiral, giving rise to a number of isomeric forms, all with the same chemical formula. For instance, galactose and glucose are both aldohexoses, but have different physical structures and chemical properties.
-
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharides () are polymeric carbohydrate molecules composed of long chains of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages, and on hydrolysis give the constituent monosaccharides or oligosaccharides. They range in structure from linear to highly branched. Examples include storage polysaccharides such as starch and glycogen, and structural polysaccharides such as cellulose and chitin.
Polysaccharides are often quite heterogeneous, containing slight modifications of the repeating unit. Depending on the structure, these macromolecules can have distinct properties from their monosaccharide building blocks. They may be amorphous or even insoluble in water. When all the monosaccharides in a polysaccharide are the same type, the polysaccharide is called a homopolysaccharide or homoglycan, but when more than one type of monosaccharide is present they are called heteropolysaccharides or heteroglycans.Natural saccharides are generally of simple carbohydrates called monosaccharides with general formula (CH2O)n where n is three or more. Examples of monosaccharides are glucose, fructose, and glyceraldehyde. Polysaccharides, meanwhile, have a general formula of Cx(H2O)y where x is usually a large number between 200 and 2500. When the repeating units in the polymer backbone are six-carbon monosaccharides, as is often the case, the general formula simplifies to (C6H10O5)n, where typically 40≤n≤3000.
As a rule of thumb, polysaccharides contain more than ten monosaccharide units, whereas oligosaccharides contain three to ten monosaccharide units; but the precise cutoff varies somewhat according to convention. Polysaccharides are an important class of biological polymers. Their function in living organisms is usually either structure- or storage-related. Starch (a polymer of glucose) is used as a storage polysaccharide in plants, being found in the form of both amylose and the branched amylopectin. In animals, the structurally similar glucose polymer is the more densely branched glycogen, sometimes called “animal starch”. Glycogen’s properties allow it to be metabolized more quickly, which suits the active lives of moving animals.
Cellulose and chitin are examples of structural polysaccharides. Cellulose is used in the cell walls of plants and other organisms, and is said to be the most abundant organic molecule on Earth. It has many uses such as a significant role in the paper and textile industries, and is used as a feedstock for the production of rayon (via the viscose process), cellulose acetate, celluloid, and nitrocellulose. Chitin has a similar structure, but has nitrogen-containing side branches, increasing its strength. It is found in arthropod exoskeletons and in the cell walls of some fungi. It also has multiple uses, including surgical threads. Polysaccharides also include callose or laminarin, chrysolaminarin, xylan, arabinoxylan, mannan, fucoidan and galactomannan.
-
Monosaccharide (noun)
A simple sugar such as glucose, fructose or deoxyribose that has a single ring.
-
Polysaccharide (noun)
A polymer made of many saccharide units linked by glycosidic bonds.
“Cellulose, starches, and complex carbohydrates, such as glycogen, are common polysaccharides in biology.”
-
Polysaccharide (noun)
a carbohydrate (e.g. starch, cellulose, or glycogen) whose molecules consist of a number of sugar molecules bonded together.
