Main Difference
The main difference between Mitosis and Meiosis is that the Mitosis is a nuclear division cycle for eukaryotic cells in which the two resulting nuclei are genetically identical and Meiosis is a One of the two nuclear divisions that occur as part of the meiotic cell cycle.
-
Mitosis
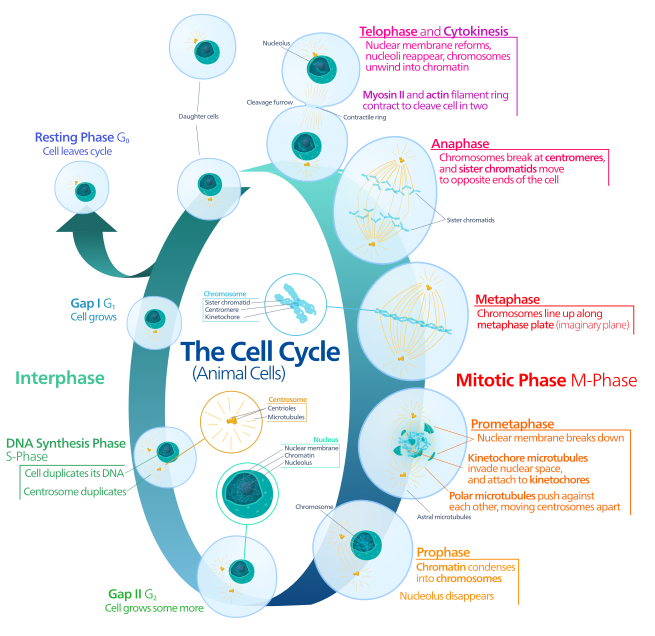
In cell biology, mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle when replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the number of chromosomes is maintained. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is preceded by the S stage of interphase (during which the DNA is replicated) and is often accompanied or followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells genetically identical to each other.
The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to spindle fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The rest of the cell may then continue to divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of the normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission. Mitosis varies between organisms. For example, animal cells undergo an “open” mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, whereas fungi undergo a “closed” mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Most human cells are produced by mitotic cell division. Important exceptions include the gametes – sperm and egg cells – which are produced by meiosis.
-
Meiosis
Meiosis ( (listen); from Greek μείωσις, meiosis, which means lessening) is a special type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, creating four haploid cells, each genetically distinct from the parent cell that gave rise to them. This process occurs in all sexually reproducing single-celled and multicellular eukaryotes, including animals, plants, and fungi. Meiotic cell divisions are an essential process during oogenesis and spermatogenesis.
Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities.In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. The two meiotic divisions are known as Meiosis I and Meiosis II. Before meiosis begins, during S phase of the cell cycle, the DNA of each chromosome is replicated so that it consists of two identical sister chromatids, which remain held together through sister chromatid cohesion. This S-phase can be referred to as “premeiotic S-phase” or “meiotic S-phase”. Immediately following DNA replication, meiotic cells enter a prolonged G2-like stage known as meiotic prophase. During this time, homologous chromosomes pair with each other and undergo genetic recombination, a programmed process in which DNA is cut and then repaired, which allows them to exchange some of their genetic information. A subset of recombination events results in crossovers, which create physical links known as chiasmata (singular: chiasma, for the Greek letter Chi (X)) between the homologous chromosomes. In most organisms, these links are essential to direct each pair of homologous chromosomes to segregate away from each other during Meiosis I, resulting in two haploid cells that have half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. During Meiosis II, the cohesion between sister chromatids is released and they segregate from one another, as during mitosis. In some cases all four of the meiotic products form gametes such as sperm, spores, or pollen. In female animals, three of the four meiotic products are typically eliminated by extrusion into polar bodies, and only one cell develops to
produce an ovum. Because the number of chromosomes is halved during meiosis, gametes can fuse (i.e. fertilization) to form a diploid
zygote that contains two copies of each chromosome, one from each parent. Thus, alternating cycles of meiosis and fertilization enable sexual reproduction, with successive generations maintaining the same number of chromosomes. For example, diploid human
cells contain 23 pairs of chromosomes including 1 pair of sex chromosomes (46 total), half of maternal origin and half of paternal origin. Meiosis produces haploid gametes (ova or sperm) that contain one set of 23 chromosomes. When two gametes (an egg and a sperm) fuse, the resulting zygote is once again diploid, with the mother and father each contributing 23 chromosomes. This same pattern, but not the same number of chromosomes, occurs in all organisms that utilize meiosis.
-
Mitosis (noun)
The division of a cell nucleus in which the genome is copied and separated into two identical halves. It is normally followed by cell division.
-
Meiosis (noun)
A figure of speech whereby something is made to seem smaller or less important than it actually is; understatement.
-
Meiosis (noun)
Cell division of a diploid cell into four haploid cells, which develop to produce gametes.
-
Mitosis (noun)
a type of cell division that results in two daughter cells each having the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent nucleus, typical of ordinary tissue growth
“the single large egg cell subdivides by repeated mitosis”
“each mitosis seems to be associated with an increase in calcium”