Main Difference
The main difference between Maltose and Maltase is that the Maltose is a chemical compound, sugar that exists in wheat and Maltase is a enzyme.
-
Maltose
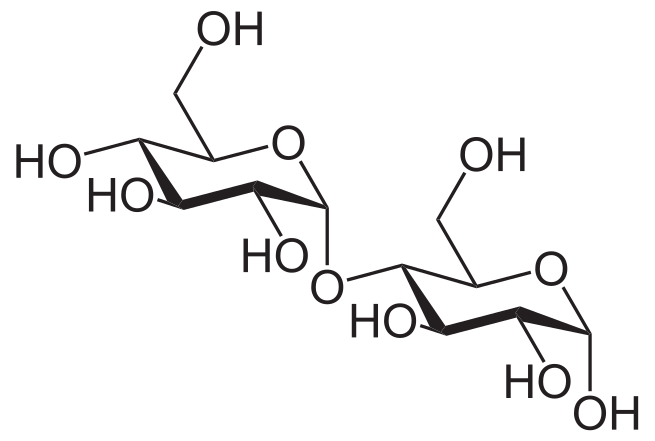
Maltose ( or ), also known as maltobiose or malt sugar, is a disaccharide formed from two units of glucose joined with an α(1→4) bond. In the isomer isomaltose, the two glucose molecules are joined with an α(1→6) bond. Maltose is the two-unit member of the amylose homologous series, the key structural motif of starch. When beta-amylase breaks down starch, it removes two glucose units at a time, producing maltose. An example of this reaction is found in germinating seeds, which is why it was named after malt. Unlike sucrose, it is a reducing sugar.
-
Maltase
Maltase (EC 3.2.1.20, alpha-glucosidase, glucoinvertase, glucosidosucrase, maltase-glucoamylase, alpha-glucopyranosidase, glucosidoinvertase, alpha-D-glucosidase, alpha-glucoside hydrolase, alpha-1,4-glucosidase, alpha-D-glucoside glucohydrolase) is an enzyme located in on the brush border of the small intestine that breaks down the disaccharide maltose. Maltase catalyzes the hydrolysis of maltose to the simple sugar glucose. This enzyme is found in plants, bacteria, and yeast. Acid maltase deficiency is categorized into three separate types based on the age of onset of symptoms in the affected individual.
In most cases, it is equivalent to alpha-glucosidase, but the term “maltase” emphasizes the disaccharide nature of the substrate from which glucose is cleaved, and “alpha-glucosidase” emphasizes the bond, whether the substrate is a disaccharide or polysaccharide.Vampire bats are the only vertebrates known to not exhibit intestinal maltase activity.
-
Maltose (noun)
A disaccharide, C12H22O11 formed from the digestion of starch by amylase; is converted to glucose by maltase; it is an isomer of trehalose
-
Maltase (noun)
An enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of maltose to glucose; often associated with amylase.
-
Maltose (noun)
a sugar produced by the breakdown of starch, e.g. by enzymes found in malt and saliva. It is a disaccharide consisting of two linked glucose units.
-
Maltase (noun)
an enzyme, present in saliva and pancreatic juice, which catalyses the breakdown of maltose and similar sugars to form glucose.
