-
Hospital
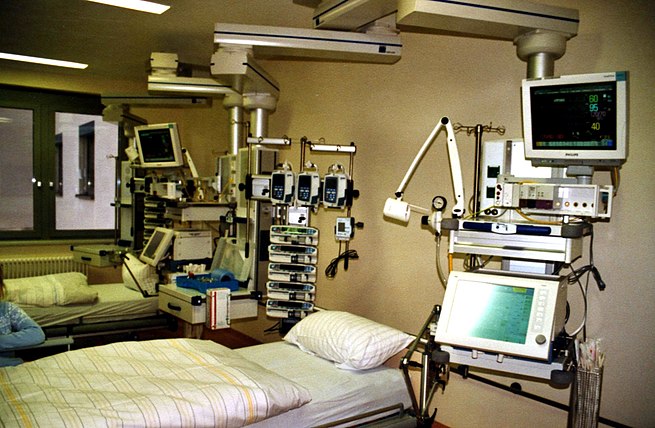
A hospital is a health care institution providing patient treatment with specialized medical and nursing staff and medical equipment. The best-known type of hospital is the general hospital, which typically has an emergency department to treat urgent health problems ranging from fire and accident victims to a heart attack. A district hospital typically is the major health care facility in its region, with a large number of beds for intensive care and additional beds for patients who need long-term care. Specialized hospitals include trauma centers, rehabilitation hospitals, children’s hospitals, seniors’ (geriatric) hospitals, and hospitals for dealing with specific medical needs such as psychiatric treatment (see psychiatric hospital) and certain disease categories. Specialized hospitals can help reduce health care costs compared to general hospitals. Hospitals are classified as general, specialty, or government depending on the sources of income received.
A teaching hospital combines assistance to people with teaching to medical students and nurses. The medical facility smaller than a hospital is generally called a clinic. Hospitals have a range of departments (e.g. surgery and urgent care) and specialist units such as cardiology. Some hospitals have outpatient departments and some have chronic treatment units. Common support units include a pharmacy, pathology, and radiology.
Hospitals are usually funded by the public sector, health organisations (for profit or nonprofit), health insurance companies, or charities, including direct charitable donations. Historically, hospitals were often founded and funded by religious orders, or by charitable individuals and leaders.Currently, hospitals are largely staffed by professional physicians, surgeons, nurses, and allied health practitioners, whereas in the past, this work was usually performed by the members of founding religious orders or by volunteers. However, there are various Catholic religious orders, such as the Alexians and the Bon Secours Sisters that still focus on hospital ministry in the late 1990s, as well as several other Christian denominations, including the Methodists and Lutherans, which run hospitals. In accordance with the original meaning of the word, hospitals were originally “places of hospitality”, and this meaning is still preserved in the names of some institutions such as the Royal Hospital Chelsea, established in 1681 as a retirement and nursing home for veteran soldiers.
-
Infirmary
A hospital is a health care institution providing patient treatment with specialized medical and nursing staff and medical equipment. The best-known type of hospital is the general hospital, which typically has an emergency department to treat urgent health problems ranging from fire and accident victims to a heart attack. A district hospital typically is the major health care facility in its region, with a large number of beds for intensive care and additional beds for patients who need long-term care. Specialized hospitals include trauma centers, rehabilitation hospitals, children’s hospitals, seniors’ (geriatric) hospitals, and hospitals for dealing with specific medical needs such as psychiatric treatment (see psychiatric hospital) and certain disease categories. Specialized hospitals can help reduce health care costs compared to general hospitals. Hospitals are classified as general, specialty, or government depending on the sources of income received.
A teaching hospital combines assistance to people with teaching to medical students and nurses. The medical facility smaller than a hospital is generally called a clinic. Hospitals have a range of departments (e.g. surgery and urgent care) and specialist units such as cardiology. Some hospitals have outpatient departments and some have chronic treatment units. Common support units include a pharmacy, pathology, and radiology.
Hospitals are usually funded by the public sector, health organisations (for profit or nonprofit), health insurance companies, or charities, including direct charitable donations. Historically, hospitals were often founded and funded by religious orders, or by charitable individuals and leaders.Currently, hospitals are largely staffed by professional physicians, surgeons, nurses, and allied health practitioners, whereas in the past, this work was usually performed by the members of founding religious orders or by volunteers. However, there are various Catholic religious orders, such as the Alexians and the Bon Secours Sisters that still focus on hospital ministry in the late 1990s, as well as several other Christian denominations, including the Methodists and Lutherans, which run hospitals. In accordance with the original meaning of the word, hospitals were originally “places of hospitality”, and this meaning is still preserved in the names of some institutions such as the Royal Hospital Chelsea, established in 1681 as a retirement and nursing home for veteran soldiers.
-
Hospital (noun)
A large medical facility, usually in a building with multiple floors, where seriously ill or injured patients are given extensive medical and/or surgical treatment.
“Luckily an ambulance arrived quickly and he was rushed to hospital.”
“Luckily an ambulance arrived quickly and he was rushed to the hospital.”
-
Hospital (noun)
A building founded for the long-term care of its residents, such as an almshouse. The residents may have no physical ailments, but simply need financial support.
-
Hospital (noun)
A place of lodging.
-
Hospital (adjective)
Hospitable.
-
Infirmary (noun)
A place where sick or injured people are cared for, especially a small hospital; sickhouse.
-
Infirmary (noun)
A clinic or dispensary within another institution.