
-
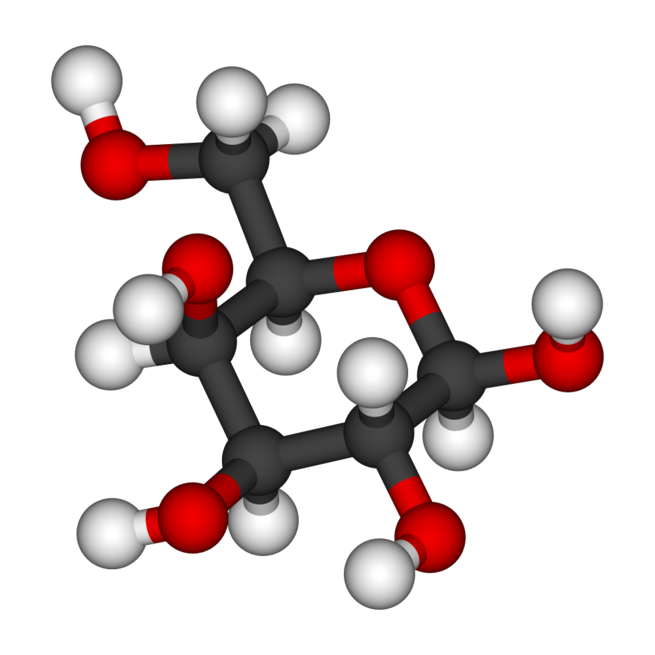
Galactose
Galactose (, galacto- + -ose, “milk sugar”), sometimes abbreviated Gal, is a monosaccharide sugar that is about as sweet as glucose, and about 65% as sweet as sucrose. It is a C-4 epimer of glucose.Galactan is a polymeric form of galactose found in hemicellulose, and forming the core of the galactans, a class of natural polymeric carbohydrates.
-
Lactose
Lactose is a disaccharide. It is a sugar composed of galactose and glucose and has the formula C12H22O11. Lactose makes up around 2–8% of milk (by weight). The name comes from lac (gen. lactis), the Latin word for milk, plus the suffix -ose used to name sugars. The compound is a white, water-soluble, non-hygroscopic solid with a mildly sweet taste. It is used in the food industry.
-
Galactose (noun)
A monosaccharide found, along with lactose, in dairy products, and is synthesized by the body where it is found associated with glycolipids and glycoproteins.
-
Lactose (noun)
The disaccharide sugar of milk and dairy products, C12H22O11, a product of glucose and galactose used as a food and in medicinal compounds.
