-
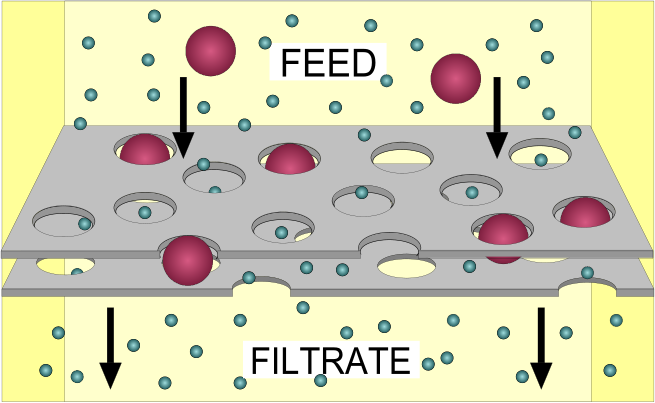
Filtration
Filtration is any of various mechanical, physical or biological operations that separate solids from fluids (liquids or gases) by adding a medium through which only the fluid can pass. The fluid that passes through is called the filtrate. In physical filters oversize solids in the fluid are retained and in biological filters particulates are trapped and ingested and metabolites are retained and removed. However, the separation is not complete; solids will be contaminated with some fluid and filtrate will contain fine particles (depending on the pore size, filter thickness and biological activity). Filtration occurs both in nature and in engineered systems; there are biological, geological, and industrial forms. For example, in animals (including humans), renal filtration removes waste from the blood, and in water treatment and sewage treatment, undesirable constituents are removed by absorption into a biological film grown on or in the filter medium, as in slow sand filtration.
-
Filtration (noun)
The act or process of filtering; the mechanical separation of a liquid from the undissolved particles floating in it.
-
Clarification (noun)
The act of impurities; particularly, the clearing or fining of liquid substances from feculent matter by the separation of the insoluble particles which prevent the liquid from being transparent.
“The clarification of wine.”
-
Clarification (noun)
The act of obscurities.
“Your ideas deserve clarification.”
-
Filtration (noun)
the action or process of filtering something
“small particles are difficult to remove without filtration”
-
Clarification (noun)
the action of making a statement or situation less confused and more comprehensible
“the remaining changes are small clarifications”
“please advise us if you require further clarification”
