-
Endoscope
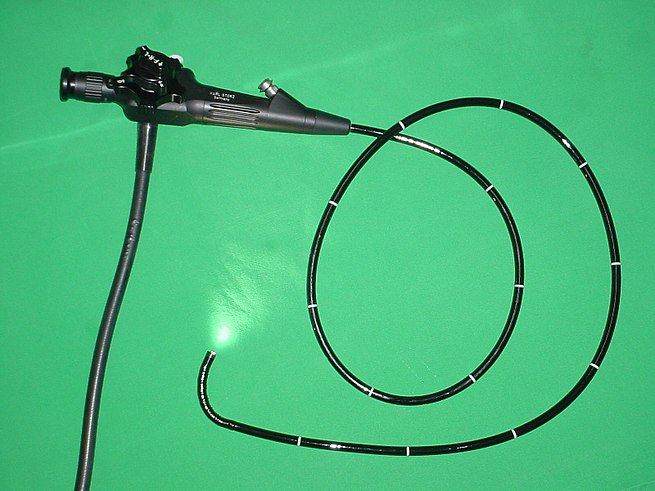
An endoscope is an illuminated optical, typically slender and tubular instrument (a type of borescope) used to look deep into the body and used in procedures called an endoscopy. “Endo” is Greek for “within” while “scope” comes from the Greek word “skopos” meaning to target or look out. It is used to examine the internal organs like the throat or esophagus. Specialized instruments are named after their target organ. Examples include the cystoscope (bladder), nephroscope (kidney), bronchoscope (bronchus), arthroscope (joints) and colonoscope (colon), and laparoscope (abdomen or pelvis). They can be used to examine visually and diagnose, or assist in surgery such as an arthroscopy.
-
Borescope
A borescope (occasionally called a boroscope, though this spelling is nonstandard) is an optical device consisting of a rigid or flexible tube with an eyepiece on one end, an objective lens on the other linked together by a relay optical system in between. The optical system in some instances is surrounded by optical fibers used for illumination of the remote object. An internal image of the illuminated object is formed by the objective lens and magnified by the eyepiece which presents it to the viewer’s eye.
Rigid or flexible borescopes may be fitted with an imaging or video device. For medical use, similar instruments are called endoscopes.
-
Endoscope (noun)
An instrument used to examine a bodily orifice or canal, or a hollow organ.
-
Borescope (noun)
An optical instrument used for seeing inside tight spaces, consisting of a rigid or flexible tube with an optical relay inside so that the view through a lens or window at one end of the tube may be seen from a lens or eyepiece in the opposite end of the tube.
