-
Embolus
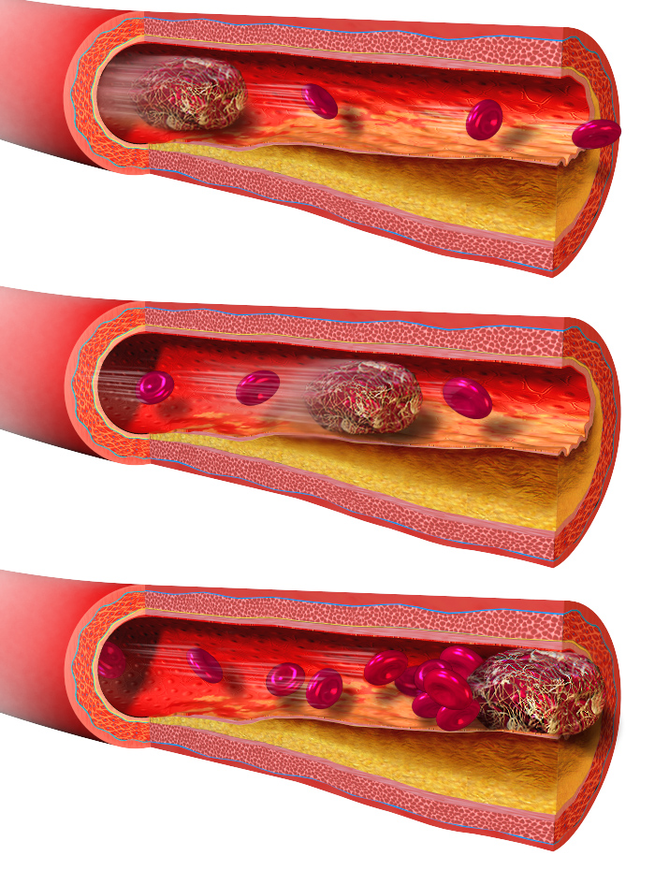
An embolus (plural emboli; from the Greek ἔμβολος “wedge”, “plug”) is an unattached mass that travels through the bloodstream and is capable of clogging arterial capillary beds (create an arterial occlusion) at a site distant from its point of origin. There are a number of different types of emboli, including blood clots, cholesterol plaque or crystals, fat globules, gas bubbles, and foreign bodies.
By contrast there are non-traveling blockages that develop locally from vascular trauma or epithelial pathology and vascular inflammation — such as atheromata and thrombi. However, if a thrombus breaks loose from its genesis site it becomes a thrombo-embolus and if not broken down during transit, may cause embolism(s).
The term was coined in 1848 by Rudolf Virchow.
-
Thrombus
A thrombus, colloquially called a blood clot, is the final product of the blood coagulation step in hemostasis. There are two components to a thrombus: aggregated platelets and red blood cells that form a plug, and a mesh of cross-linked fibrin protein. The substance making up a thrombus is sometimes called cruor. A thrombus is a healthy response to injury intended to prevent bleeding, but can be harmful in thrombosis, when clots obstruct blood flow through healthy blood vessels.
Mural thrombi are thrombi that adhere to the wall of a blood vessel. They occur in large vessels such as the heart and aorta, and can restrict blood flow but usually do not block it entirely. They appear grey-red with alternating light and dark lines (known as lines of Zahn) which represent bands of fibrin (lighter) with entrapped white blood cells and red blood cells (darker).
-
Embolus (noun)
An obstruction causing an embolism: a blood clot, air bubble or other matter carried by the bloodstream and causing a blockage or occlusion of a blood vessel.
-
Embolus (noun)
The structure on the end of the palp of male arachnids which contains the opening to the ejaculatory duct.
-
Thrombus (noun)
A blood clot formed from platelets and other elements; that forms in a blood vessel in a living organism, and causes thrombosis or obstruction of the vessel at its point of formation or travel to other areas of the body.
