Main Difference
The main difference between Cytoplasm and Protoplasm is that the Cytoplasm is a All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures and Protoplasm is a part of cell
-
Cytoplasm
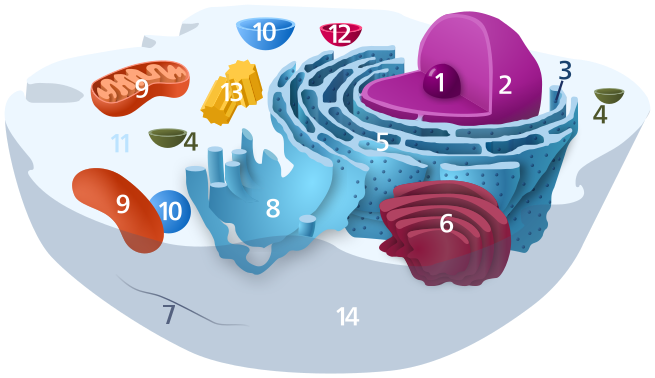
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is the material within a living cell, excluding the cell nucleus. It comprises cytosol (the gel-like substance enclosed within the cell membrane) and the organelles – the cell’s internal sub-structures. All of the contents of the cells of prokaryotic organisms (such as bacteria, which lack a cell nucleus) are contained within the cytoplasm. Within the cells of eukaryotic organisms the contents of the cell nucleus are separated from the cytoplasm, and are then called the nucleoplasm. The cytoplasm is about 80% water and usually colorless.
The submicroscopic ground cell substance or cytoplasmatic matrix which remains after exclusion the cell organelles and particles is groundplasm. It is the hyaloplasm of light microscopy, and high complex, polyphasic system in which all of resolvable cytoplasmic elements of are suspended, including the larger organelles such as the ribosomes, mitochondria, the plant plastids, lipid droplets, and vacuoles.
It is within the cytoplasm that most cellular activities occur, such as many metabolic pathways including glycolysis, and processes such as cell division. The concentrated inner area is called the endoplasm and the outer layer is called the cell cortex or the ectoplasm.
Movement of calcium ions in and out of the cytoplasm is a signaling activity for metabolic processes.
In plants, movement of the cytoplasm around vacuoles is known as cytoplasmic streaming.
-
Protoplasm
Protoplasm is the living content of a cell that is surrounded by a plasma membrane.
In some definitions, it is a general term for the cytoplasm (e.g., Mohl, 1846), but for others, it also includes the nucleoplasm (e.g., Strasburger, 1882). For Sharp (1921), “According to the older usage the extra-nuclear portion of the protoplast [the entire cell, excluding the cell wall] was called “protoplasm,” but the nucleus also is composed of protoplasm, or living substance in its broader sense. The current consensus is to avoid this ambiguity by employing Strasburger’s [(1882)] terms cytoplasm [coined by Kölliker (1863), originally as synonym for protoplasm] and nucleoplasm ([term coined by van Beneden (1875), or] karyoplasm, [used by] Flemming [(1878)])”. The cytoplasm definition of Strasburger excluded the plastids (Chromatoplasm).
Like the nucleus, whether to include the vacuole in the protoplasm concept is controversial.
-
Cytoplasm (noun)
The contents of a cell except for the nucleus. It includes cytosol, organelles, vesicles, and the cytoskeleton.
-
Protoplasm (noun)
The entire contents of a cell comprising the nucleus and the cytoplasm. It is a semi-fluid, transparent substance which is the living matter of plant and animal cells.
