-
Cyclohexane
Cyclohexane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula C6H12. Cyclohexane is a colourless, flammable liquid with a distinctive detergent-like odor, reminiscent of cleaning products (in which it is sometimes used). Cyclohexane is mainly used for the industrial production of adipic acid and caprolactam, which are precursors to nylon.Cyclohexyl is the alkyl substituent of cyclohexane and is abbreviated Cy.
-
Hexane
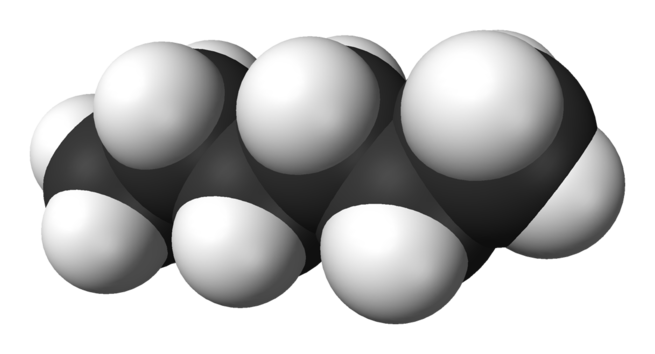
Hexane is an alkane of six carbon atoms, with the chemical formula C6H14.
The term may refer to any of the five structural isomers with that formula, or to a mixture of them. In IUPAC nomenclature, however, hexane is the unbranched isomer (n-hexane); the other four isomers are named as methylated derivatives of pentane and butane. IUPAC also uses the term as the root of many compounds with a linear six-carbon backbone, such as 2-methylhexane.
Hexanes are significant constituents of gasoline. They are all colorless liquids, odorless when pure, with boiling points between 50 and 70 °C (122 and 158 °F). They are widely used as cheap, relatively safe, largely unreactive, and easily evaporated non-polar solvents.
-
Cyclohexane (noun)
An alicyclic hydrocarbon, C6H12, consisting of a ring of six carbon atoms; a volatile liquid.
-
Hexane (noun)
Any of five isomeric aliphatic hydrocarbons, C6H14. They are colorless, volatile liquids.
-
Cyclohexane (noun)
a colourless flammable liquid cycloalkane obtained from petroleum or by hydrogenating benzene, and used as a solvent and paint remover.
-
Hexane (noun)
a colourless liquid hydrocarbon of the alkane series, present in petroleum spirit.
