-
Engine
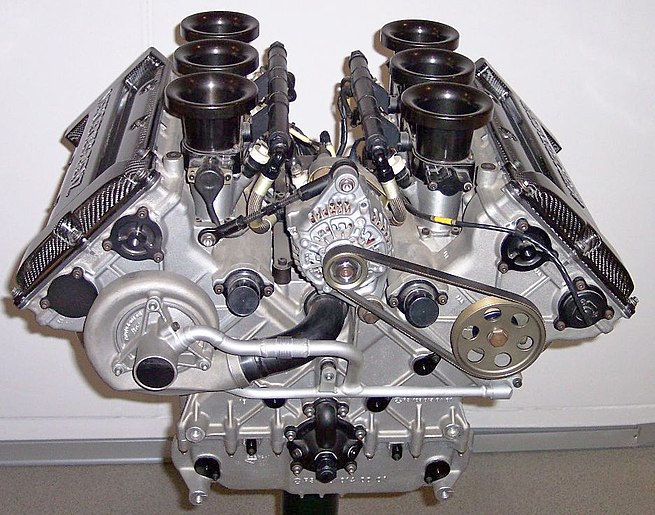
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one form of energy into mechanical energy. Heat engines burn a fuel to create heat which is then used to do work. Internal combustion engines are heat engines that burn fuel in a combustion chamber to extract work from the pressure of expanding gases. Electric motors convert electrical energy into mechanical motion; pneumatic motors use compressed air; and clockwork motors in wind-up toys use elastic energy. In biological systems, molecular motors, like myosins in muscles, use chemical energy to create forces and eventually motion.
-
Cunning (adjective)
Sly; crafty; clever in surreptitious behaviour.
-
Cunning (adjective)
Skillful, artful.
-
Cunning (adjective)
Wrought with, or exhibiting, skill or ingenuity; ingenious.
“cunning work”
-
Cunning (adjective)
Cute, appealing.
“a cunning little boy””
-
Cunning (noun)
Practical knowledge or experience; aptitude in performance; skill, proficiency; dexterity.
-
Cunning (noun)
Practical skill employed in a secret or crafty manner; craft; artifice; skillful deceit.
-
Cunning (noun)
The disposition to employ one’s skill in an artful manner; craftiness; guile; artifice; skill of being cunning, sly, conniving, or deceitful.
-
Cunning (noun)
The natural wit or instincts of an animal.
“the cunning of the fox or hare”
-
Cunning (noun)
Knowledge; learning; special knowledge (sometimes implying occult or magical knowledge).
-
Engine (noun)
A large construction used in warfare, such as a battering ram, catapult etc. from 14th c.
-
Engine (noun)
A tool; a utensil or implement. from 14th c.
-
Engine (noun)
A complex mechanical device which converts energy into useful motion or physical effects. from 16th c.
-
Engine (noun)
A person or group of people which influence a larger group; a driving force. from 16th c.
-
Engine (noun)
The part of a car or other vehicle which provides the force for motion, now especially one powered by internal combustion. from 19th c.
-
Engine (noun)
A self-powered vehicle, especially a locomotive, used for pulling cars along a track. from 19th c.
-
Engine (noun)
A software or hardware system responsible for a specific technical task (usually with qualifying word). from 20th c.
“a graphics engine; a physics engine”
-
Engine (noun)
Ingenuity; cunning, trickery, guile. 13th-17th c.
-
Engine (noun)
The result of cunning; something ingenious, a contrivance; (in negative senses) a plot, a scheme. 13th-18th c.
-
Engine (noun)
Natural talent; genius. 14th-17th c.
-
Engine (noun)
Anything used to effect a purpose; any device or contrivance; an agent.
-
Engine (verb)
To equip with an engine; said especially of steam vessels.
“Vessels are often built by one firm and engined by another.”
-
Engine (verb)
To assault with an engine.
-
Engine (verb)
To contrive; to put into action.
-
Engine (verb)
To rack; to torture.
-
Engine (noun)
a machine with moving parts that converts power into motion
“engine failure”
“the roar of a car engine”
-
Engine (noun)
a thing that is the agent or instrument of a particular process
“exports used to be the engine of growth”
-
Engine (noun)
a locomotive.
-
Engine (noun)
a fire engine.
-
Engine (noun)
a mechanical device or instrument, especially one used in warfare
“a siege engine”