Main Difference
The main difference between Atopy and Anaphylaxis is that the Atopy is a predisposition towards allergy and Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction
-
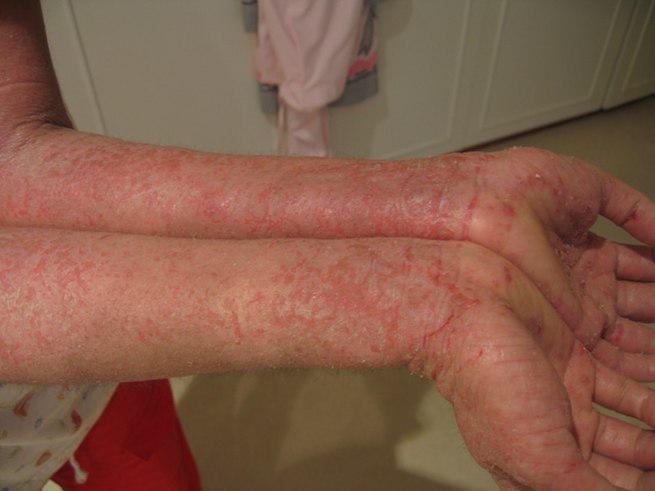
Atopy
Atopy is the tendency to produce an exaggerated IgE immune response to otherwise harmless environmental substances, while an allergic disease can be defined as the clinical manifestation of this inappropriate IgE immune response.Atopy may have a hereditary component, although contact with the allergen or irritant must occur before the hypersensitivity reaction can develop. Maternal psychological trauma in utero may also be a strong indicator for development of atopy.The term atopy was coined by Coca and Cooke in 1923. Many physicians and scientists use the term “atopy” for any IgE-mediated reaction (even those that are appropriate and proportional to the antigen), but many pediatricians reserve the word “atopy” for a genetically mediated predisposition to an excessive IgE reaction. The term is from Greek ἀτοπία meaning “the state of being out of place”, “absurdity”.
-
Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a serious allergic reaction that is rapid in onset and may cause death. It typically causes more than one of the following: an itchy rash, throat or tongue swelling, shortness of breath, vomiting, lightheadedness, and low blood pressure. These symptoms typically come on over minutes to hours.Common causes include insect bites and stings, foods, and medications. Other causes include latex exposure and exercise. Additionally, cases may occur without an obvious reason. The mechanism involves the release of mediators from certain types of white blood cells triggered by either immunologic or non-immunologic mechanisms. Diagnosis is based on the presenting symptoms and signs after exposure to a potential allergen.The primary treatment of anaphylaxis is epinephrine injection into a muscle, intravenous fluids, and positioning the person flat. Additional doses of epinephrine may be required. Other measures, such as antihistamines and steroids, are complementary. Carrying an epinephrine autoinjector and identification regarding the condition is recommended in people with a history of anaphylaxis.Worldwide, 0.05–2% of the population is estimated to experience anaphylaxis at some point in life. Rates appear to be increasing. It occurs most often in young people and females. Of people who go to a hospital with anaphylaxis in the United States about 99.7% survive. The term comes from the Ancient Greek: ἀνά, romanized: ana, lit. ‘against’, and the Ancient Greek: φύλαξις, romanized: phylaxis, lit. ‘protection’.
-
Atopy (noun)
A hereditary disorder marked by the tendency to develop localized immediate hypersensitivity reactions to allergens such as pollen, food etc and is manifested by hay fever, asthma, or similar allergic conditions; generally considered to be caused by the interaction of environmental and genetic factors.
-
Atopy (noun)
A person suffering from atopic syndrome; a case of atopy.
-
Anaphylaxis (noun)
Extreme sensitivity to a substance such as a foreign protein or drug.
-
Anaphylaxis (noun)
A severe and rapid systemic allergic reaction to an allergen, causing a constriction of the trachea, preventing breathing; anaphylactic shock.
