-
Ascus
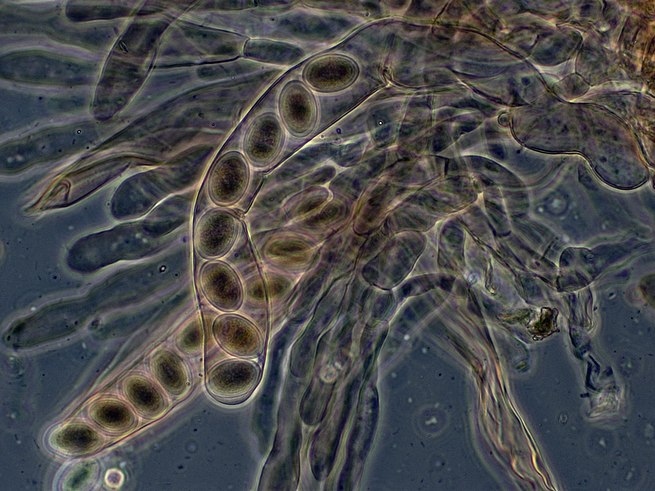
An ascus (plural asci; from Greek ἀσκός ảskós ‘skin bag’) is the sexual spore-bearing cell produced in ascomycete fungi. Asci usually contain eight ascospores, produced by meiosis followed, in most species, by a mitotic cell division. However, asci in some genera or species can occur in numbers of one (e.g. Monosporascus cannonballus), two, four, or multiples of four. In a few cases, the ascospores can bud off conidia that may fill the asci (e.g. Tympanis) with hundreds of conidia, or the ascospores may fragment, e.g. some Cordyceps, also filling the asci with smaller cells. Ascospores are nonmotile, usually single celled, but not infrequently may be coenocytic (lacking a septum), and in some cases coenocytic in multiple planes. Mitotic divisions within the developing spores populate each resulting cell in septate ascospores with nuclei. The term ocular chamber, or oculus, refers to the epiplasm (the portion of cytoplasm not used in ascospore formation) that is surrounded by the “bourrelet” (the thickened tissue near the top of the ascus).In many cases the asci are formed in a regular layer, the hymenium, in a fruiting body which is visible to the naked eye, here called an ascocarp or ascoma. In other cases, such as single-celled yeasts, no such structures are found. In rare cases asci of some genera can regularly develop inside older discharged asci one after another, e.g. Dipodascus.
Asci normally release their spores by bursting at the tip, but they may also digest themselves passively releasing the ascospores either in a liquid or as a dry powder. Discharging asci usually have a specially differentiated tip, either a pore or an operculum. In some hymenium forming genera, when one ascus bursts, it can trigger the bursting of many other asci in the ascocarp resulting in a massive discharge visible as a cloud of spores – the phenomenon called “puffing”. This is an example of positive feedback. A faint hissing sound can also be heard for species of Peziza and other cup fungi.
Asci, notably those of Neurospora crassa, have been used in laboratories for studying the process of meiosis, because the four cells produced by meiosis line up in regular order. By modifying genes coding for spore color and nutritional requirements, the biologist can study crossing over and other phenomena. The formation of asci and their use in genetic analysis are described in detail in Neurospora crassa.
Asci of most Pezizomycotina develop after the formation of croziers at their base. The croziers help maintain a brief dikaryon. The compatible nuclei of the dikaryon merge forming a diploid nucleus that then undergoes meiosis and ultimately internal ascospore formation. Members of the Taphrinomycotina and Saccharomycotina do not form croziers.
-
Basidium
A basidium (pl., basidia) is a microscopic sporangium (or spore-producing structure) found on the hymenophore of fruiting bodies of basidiomycete fungi which are also called tertiary mycellium, developed from secondary mycelium. Tertiary mycelium is highly coiled secondary mycelium, a dikaryon. The presence of basidia is one of the main characteristic features of the Basidiomycota. A basidium usually bears four sexual spores called basidiospores; occasionally the number may be two or even eight. In a typical basidium, each basidiospore is borne at the tip of a narrow prong or horn called a sterigma (pl. sterigmata), and is forcibly discharged upon maturity.
The word basidium literally means little pedestal, from the way in which the basidium supports the spores. However, some biologists suggest that the structure more closely resembles a club. An immature basidium is known as a basidiole.
-
Ascus (noun)
A sac-shaped cell present in ascomycete fungi; it is a reproductive cell in which meiosis and an additional cell division produce eight spores.
-
Basidium (noun)
A small structure, shaped like a club, found in the Basidiomycota division of fungi, that bears four spores at the tips of small projections.
