Main Difference
The main difference between Anatomy and Biology is that the Anatomy is a branch of biology and medicine that considers the structure of living things and Biology is a study of life
-
Anatomy
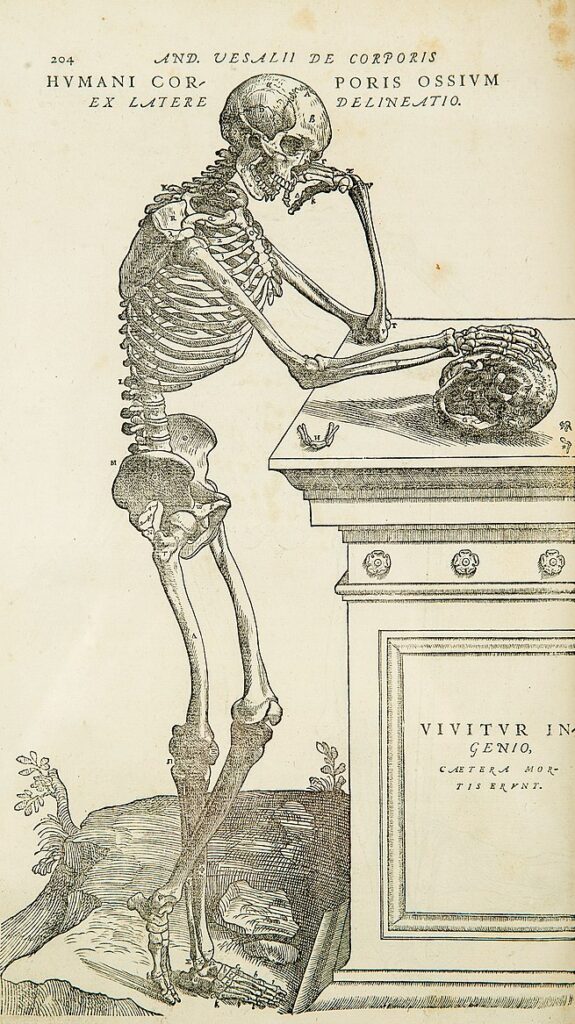
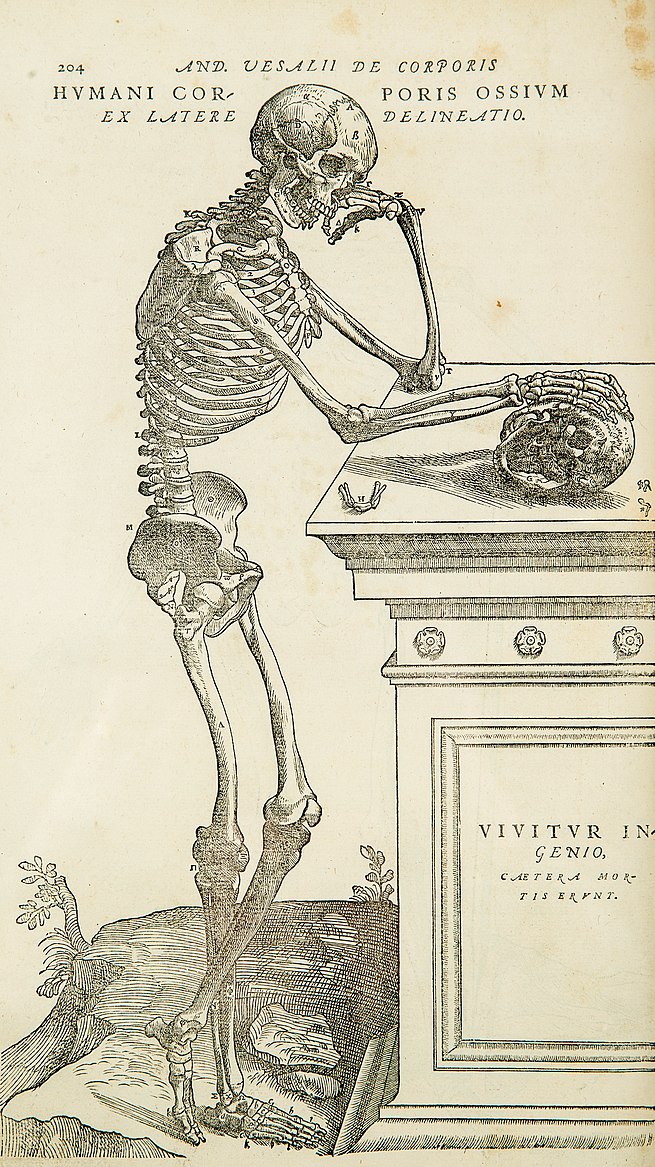
Anatomy (Greek anatomē, “dissection”) is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science which deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Anatomy is inherently tied to developmental biology, embryology, comparative anatomy, evolutionary biology, and phylogeny, as these are the processes by which anatomy is generated over immediate (embryology) and long (evolution) timescales. Anatomy and physiology, which study (respectively) the structure and function of organisms and their parts, make a natural pair of related disciplines, and they are often studied together. Human anatomy is one of the essential basic sciences that are applied in medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology, and also in the study of cells.
The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.
-
Biology
Biology is the natural science that studies life and living organisms, including their physical structure, chemical processes, molecular interactions, physiological mechanisms, development and evolution. Despite the complexity of the science, there are certain unifying concepts that consolidate it into a single, coherent field. Biology recognizes the cell as the basic unit of life, genes as the basic unit of heredity, and evolution as the engine that propels the creation and extinction of species. Living organisms are open systems that survive by transforming energy and decreasing their local entropy to maintain a stable and vital condition defined as homeostasis.Sub-disciplines of biology are defined by the research methods employed and the kind of system studied: theoretical biology uses mathematical methods to formulate quantitative models while experimental biology performs empirical experiments to test the validity of proposed theories and understand the mechanisms underlying life and how it appeared and evolved from non-living matter about 4 billion years ago through a gradual increase in the complexity of the system. See branches of biology.
-
Anatomy (noun)
The art of studying the different parts of any organized body, to discover their situation, structure, and economy.
“dissection”
-
Anatomy (noun)
The science that deals with the form and structure of organic bodies; anatomical structure or organization.
“anthropotomy|phytotomy|zootomy”
“Animal anatomy is also called zootomy; vegetable anatomy, phytotomy; and human anatomy, anthropotomy.”
-
Anatomy (noun)
A treatise or book on anatomy.
-
Anatomy (noun)
The act of dividing anything, corporeal or intellectual, for the purpose of examining its parts.
“analysis”
“the anatomy of a discourse”
“the anatomy of love”
“Burton’s famous treatise, “The Anatomy of Melancholy””
-
Anatomy (noun)
The form of an individual.
“I went to the Venice beach body-building competition and noticed the competitor from Athens, and let me tell you, that’s what I call classic Greek anatomy.”
-
Anatomy (noun)
The human body, especially in reference to the private parts.
-
Anatomy (noun)
A skeleton, or dead body.
-
Anatomy (noun)
The physical or functional organization of an organism, or part of it.
-
Biology (noun)
The study of all life or living matter.
-
Biology (noun)
The living organisms of a particular region.
-
Biology (noun)
The structure, function, and behavior of an organism or type of organism.
“the biology of the whale”
-
Biology (noun)
the study of living organisms, divided into many specialized fields that cover their morphology, physiology, anatomy, behaviour, origin, and distribution.
-
Biology (noun)
the plants and animals of a particular area
“the biology of the Chesapeake Bay”
-
Biology (noun)
the physiology, behaviour, and other qualities of a particular organism or class of organisms
“human biology”