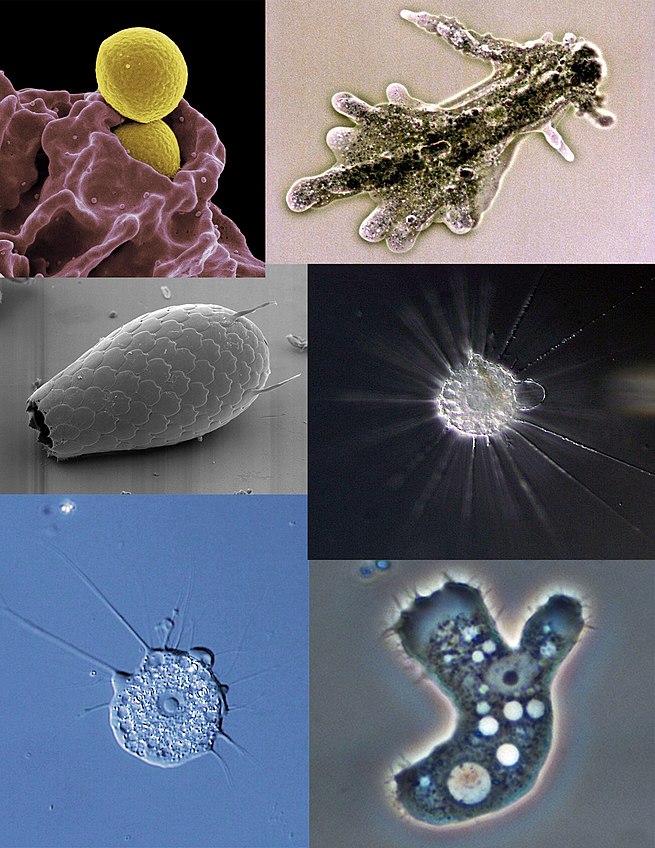
Main Difference
The main difference between Amoeba and Euglena is that the Amoeba is a polyphyletic group including different eucariot taxons and Euglena is a genus of unicellular flagellate protists
-
Amoeba
An amoeba (; rarely spelled amœba; plural am(o)ebas or am(o)ebae ), often called amoeboid, is a type of cell or unicellular organism which has the ability to alter its shape, primarily by extending and retracting pseudopods. Amoebas do not form a single taxonomic group; instead, they are found in every major lineage of eukaryotic organisms. Amoeboid cells occur not only among the protozoa, but also in fungi, algae, and animals.Microbiologists often use the terms “amoeboid” and “amoeba” interchangeably for any organism that exhibits amoeboid movement.In older classification systems, most amoebas were placed in the class or subphylum Sarcodina, a grouping of single-celled organisms that possess pseudopods or move by protoplasmic flow. However, molecular phylogenetic studies have shown that Sarcodina is not a monophyletic group whose members share common descent. Consequently, amoeboid organisms are no longer classified together in one group.The best known amoeboid protists are the “giant amoebae” Chaos carolinense and Amoeba proteus, both of which have been widely cultivated and studied in classrooms and laboratories. Other well known species include the so-called “brain-eating amoeba” Naegleria fowleri, the intestinal parasite Entamoeba histolytica, which causes amoebic dysentery, and the multicellular “social amoeba” or slime mould Dictyostelium discoideum.
-
Euglena
Euglena is a genus of single cell flagellate eukaryotes. It is the best known and most widely studied member of the class Euglenoidea, a diverse group containing some 54 genera and at least 800 species. Species of Euglena are found in freshwater and salt water. They are often abundant in quiet inland waters where they may bloom in numbers sufficient to color the surface of ponds and ditches green (E. viridis) or red (E. sanguinea).The species Euglena gracilis has been used extensively in the laboratory as a model organism.Most species of Euglena have photosynthesizing chloroplasts within the body of the cell, which enable them to feed by autotrophy, like plants. However, they can also take nourishment heterotrophically, like animals. Since Euglena have features of both animals and plants, early taxonomists, working within the Linnaean two-kingdom system of biological classification, found them difficult to classify. It was the question of where to put such “unclassifiable” creatures that prompted Ernst Haeckel to add a third living kingdom (a fourth kingdom in toto) to the Animale, Vegetabile (and Lapideum meaning Mineral) of Linnaeus: the Kingdom Protista.
-
Amoeba (noun)
A member of the genus Amoeba of unicellular protozoa that moves by means of temporary projections called pseudopodia.
-
Amoeba (noun)
The graph of the real part of the logarithms of a polynomial equation in complex numbers.
-
Amoeba (noun)
An asexual.
-
Euglena (noun)
Any of several protists, of the genus Euglena, that contain chloroplasts and a single flagellum
