Main Difference
The main difference between Nerve and Neuron is that the Nerve is a enclosed, cable-like bundle of axons in the peripheral nervous system and Neuron is a electrically excitable cell.
-
Nerve
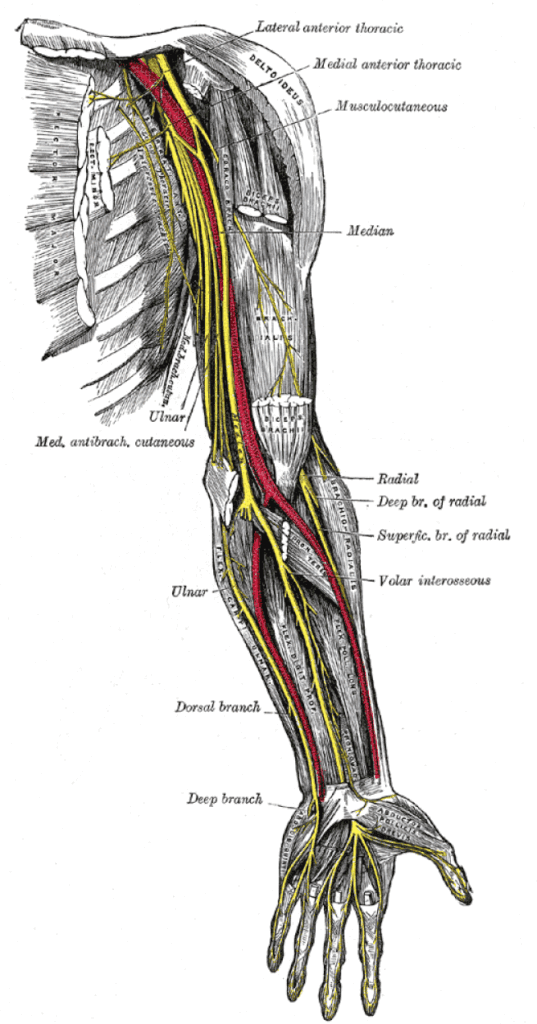
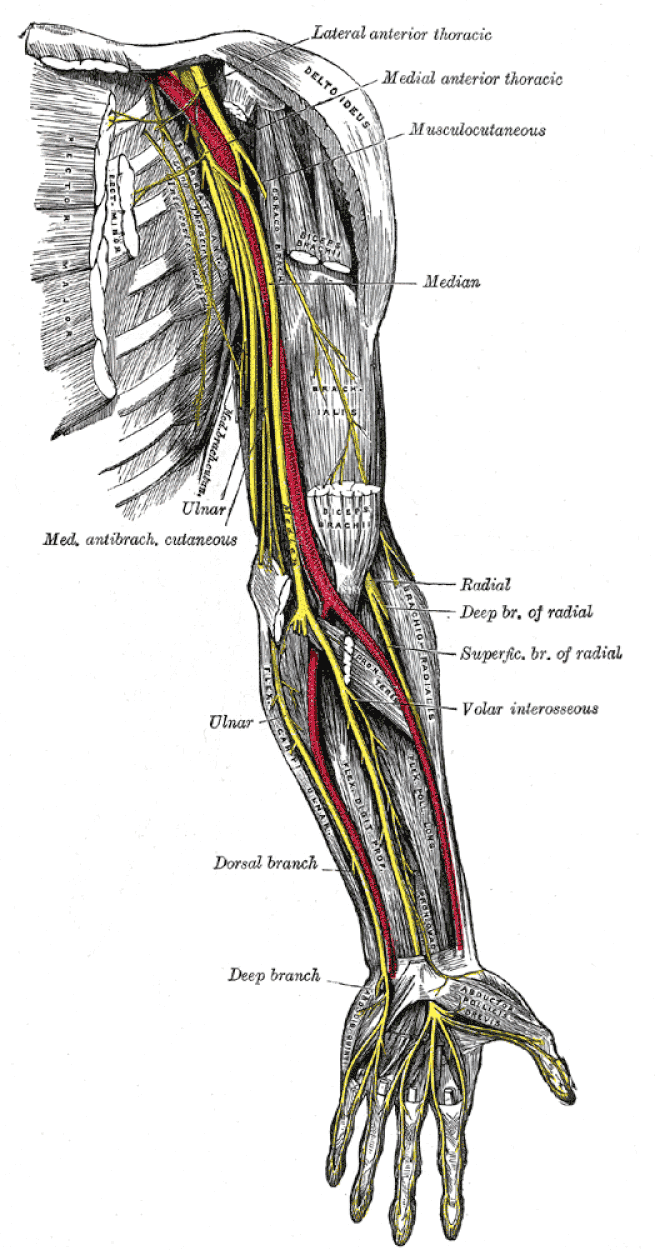
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of axons (nerve fibers, the long and slender projections of neurons) in the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the electrochemical nerve impulses that are transmitted along each of the axons to peripheral organs.
In the central nervous system, the analogous structures are known as tracts. Neurons are sometimes called nerve cells, though this term is potentially misleading since many neurons do not form nerves, and nerves also include non-neuronal Schwann cells that coat the axons in myelin.
Each nerve is a cordlike structure containing bundles of axons. Within a nerve, each axon is surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called the endoneurium. The axons are bundled together into groups called fascicles, and each fascicle is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the perineurium. Finally, the entire nerve is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the epineurium.
-
Neuron
A neuron, also known as a neurone (British spelling) and nerve cell, is an electrically excitable cell that receives, processes, and transmits information through electrical and chemical signals. These signals between neurons occur via specialized connections called synapses. Neurons can connect to each other to form neural circuits. Neurons are the primary components of the central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord, and of the peripheral nervous system, which comprises the autonomic nervous system and the somatic nervous system.
There are many types of specialized neurons. Sensory neurons respond to one particular type of stimulus such as touch, sound, or light and all other stimuli affecting the cells of the sensory organs, and converts it into an electrical signal via transduction, which is then sent to the spinal cord or brain. Motor neurons receive signals from the brain and spinal cord to control everything from muscle contractions to glandular output. Interneurons connect neurons to other neurons within the same region of the brain or spinal cord in neural networks.
A typical neuron consists of a cell body (soma), dendrites, and an axon. The term neurite is used to describe either a dendrite or an axon, particularly in its undifferentiated stage. Dendrites are thin structures that arise from the cell body, often extending for hundreds of micrometers and branching multiple times, giving rise to a complex “dendritic tree”. An axon (also called a nerve fiber) is a special cellular extension (process) that arises from the cell body at a site called the axon hillock and travels for a distance, as far as 1 meter in humans or even more in other species. Most neurons receive signals via the dendrites and send out signals down the axon. Numerous axons are often bundled into fascicles that make up the nerves in the peripheral nervous system (like strands of wire make up cables). Bundles of axons in the central nervous system are called tracts. The cell body of a neuron frequently gives rise to multiple dendrites, but never to more than one axon, although the axon may branch hundreds of times before it terminates. At the majority of synapses, signals are sent from the axon of one neuron to a dendrite of another. There are, however, many exceptions to these rules: for example, neurons can lack dendrites, or have no axon, and synapses can connect an axon to another axon or a dendrite to another dendrite.
All neurons are electrically excitable, due to maintenance of voltage gradients across their membranes by means of metabolically driven ion pumps, which combine with ion channels embedded in the membrane to generate intracellular-versus-extracellular concentration differences of ions such as sodium, potassium, chloride, and calcium. Changes in the cross-membrane voltage can alter the function of voltage-dependent ion channels. If the voltage changes by a large enough amount, an all-or-none electrochemical pulse called an action potential is generated and this change in cross-membrane potential travels rapidly along the cell’s axon, and activates synaptic connections with other cells when it arrives.
In most cases, neurons are generated by special types of stem cells during brain development and childhood. Neurons in the adult brain generally do not undergo cell division. Astrocytes are star-shaped glial cells that have also been observed to turn into neurons by virtue of the stem cell characteristic pluripotency. Neurogenesis largely ceases during adulthood in most areas of the brain. However, there is strong evidence for generation of substantial numbers of new neurons in two brain areas, the hippocampus and olfactory bulb.
-
Nerve (noun)
A bundle of neurons with their connective tissue sheaths, blood vessels and lymphatics.
“The nerves can be seen through the skin.”
-
Nerve (noun)
A neuron.
-
Nerve (noun)
A vein in a leaf; a grain in wood
“Some plants have ornamental value because of their contrasting nerves.”
-
Nerve (noun)
Courage, boldness.
“He hasn’t the nerve to tell her he likes her. What a wimp!”
-
Nerve (noun)
Patience. en
-
Nerve (noun)
Stamina, endurance, fortitude.
-
Nerve (noun)
Audacity, gall.
“He had the nerve to enter my house uninvited.”
-
Nerve (noun)
The elastic resistance of raw rubber or other polymers to permanent deformation during processing.
“A nervy tank lining will be difficult to lay around tight bends or in corners because it tends to spring back.Blair Rubber company glossary of terms. [https://blairrubber.com/wp-content/uploads/glossary-of-terms.pdf]“
-
Nerve (noun)
Agitation caused by fear, stress or other negative emotion.
“Ellie had a bad case of nerves before the big test.”
-
Nerve (noun)
Sinew, tendon.
-
Nerve (verb)
To give courage.
“May their example nerve us to face the enemy.”
-
Nerve (verb)
To give strength.
“The liquor nerved up several of the men after their icy march.”
-
Neuron (noun)
A cell of the nervous system, which conducts nerve impulses; consisting of an axon and several dendrites. Neurons are connected by synapses.
-
Neuron (noun)
A nervure of an insect’s wing.